Chemical and heat resistance
Chemical resistance of MEF™
Thanks to its excellent chemical resistance, MEF™ can be used for a wide variety of applications.
| Chemical | Rating |
|---|---|
| Hydrochloric acid (10%) | ◎ |
| Hydrochloric acid (36%) | ◎ |
| Sulfuric acid (10%) | ◎ |
| Sulfuric acid (30%) | ◎ |
| Nitric acid (10%) | ◎ |
| Nitric acid (40%) | ◎ |
| Phosphoric acid | ◯ |
| Boric acid | ◎ |
| Potassium hydroxide (10%) | ◎ |
| Sodium hydroxide (10%) | ◎ |
| Calcium hydroxide (10%) | ◎ |
| Hydrogen peroxide (3%) | ◎ |
| Chemical | Rating |
|---|---|
| Aqueous ammonia | ◎ |
| n-Heptane | △ |
| Toluene | △ |
| Ethylene dioxide | ◯ |
| Trichloroethylene | △ |
| Chloroform | ◯ |
| Acetone | ◎ |
| Methyl acetate water | ◎ |
| Ethyl alcohol | ◎ |
| Chemical | Rating |
|---|---|
| Gasoline | ◯ |
| Gas oil | ◎ |
| Kerosene | ◯ |
| Fuel oil | ◎ |
| Turpentine oil | △ |
| Engine oil | ◯ |
| Turbine oil | ◯ |
| Linseed oil | ◎ |
Test method (ASTM D 543-56T)
The test piece (75 mm×25 mm×10 mm) is left immersed in various chemical products for 7 days in an atmosphere of 23°C and 50% RH. It is then removed from the chemical product and left at 35°C for 24 hours. The changes in dimensions and mass are then measured.
Rating
| Rating | Dimensional change rate (%) | Chemical absorption rate (Vol %) | Appearance |
|---|---|---|---|
| ◎ | < 1 | < 3 | No change |
| ◯ | 1 〜 3 | 3 〜10 | Little change |
| △ | > 3 | > 10 | Swelling |
| × | Dissolution or contraction |
Comparison of chemical resistance
| Chemical | MEF™ | Expanding polystyrene |
|---|---|---|
| Kerosene | ◯ | × |
| Engine oil | ◯ | × |
| Gasoline | ◯ | × |
| Toluene | △ | × |
| Trichloroethylene | △ | × |
| Acetone | ◎ | × |
| Methyl acetate | ◎ | × |
| Ethyl alcohol | ◎ | ◎ |
| linseed oil | ◎ | × |
Cold resistance of MEF™
Since the principal raw material used to make MEF™ is polyethylene, a foam product, resistance to cold is excellent.
Even at low temperatures, resistance to cracking and chipping is high.

Tensile elongation rate at low temperatures (-30℃)
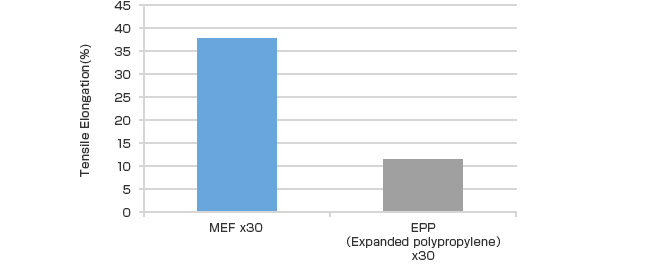
Note: The values in this table are measurement results; they are not intended as specifications.
