PHOSPHOFRUCTOKINASE [PFKWⅡ]
from Geobacillus stearothermophilus
(ATP: D–fructose–6–phosphate–1–phosphotransferase, EC 2.7.1.11)
ATP + D–Fructose–6–phosphate → ADP + D–Fructose–1,6–bisphosphate
Preparation and Specification
- Appearance
- : White to pale yellowish amorphous powder, lyophilized
- Specific activity
- : More than 150 U/mg solid
- Contaminants
- : ATPase Less than 0.005% (U/U)
- : NADPHox Less than 0.010% (U/U)
Properties
- Molecular weight
- : 72 kDa (gel filtration)
35 kDa (SDS–PAGE)
- Isoelectric point
- : pH 5.9
- Michaelis constants
- : D–Fructose–6–phosphate (D–F–6–P) 5.8 mM (at 37℃)
ATP 0.07 mM (at 37℃)
- Optimum pH
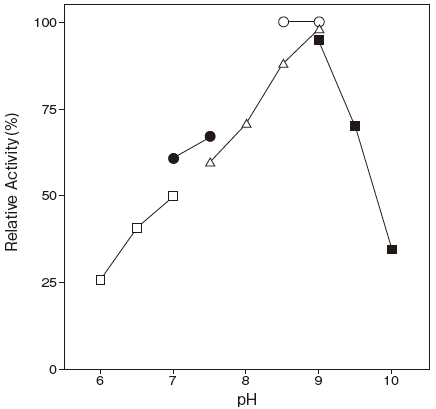
- : 9.0Figure 1
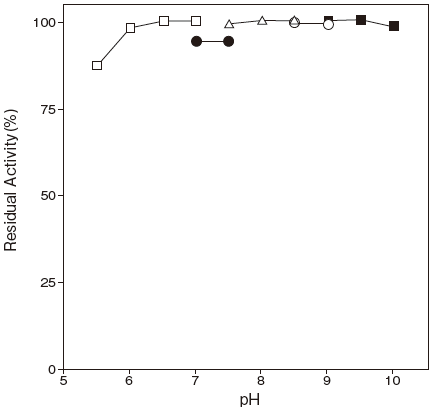
- pH stability
- : 6.0–10.0 (37℃, 1 hr.) Figure 2
- Thermal stability
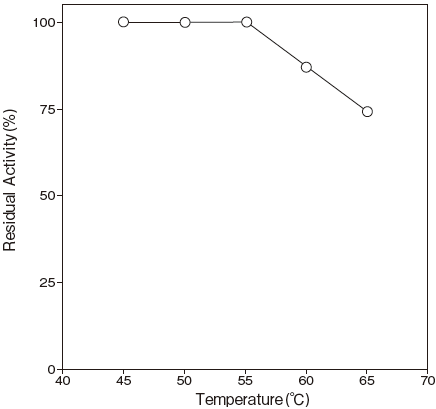
- : Stable at 55℃ and below (pH8.5, 30min) Figure3
- Activators
- : Mg2+
Applications for Diagnostic Test
This enzyme is useful for enzymatic determination of F–6–P.
| PFKWⅡ | ||
| ATP+D-F-6-P | → | ADP+D-Fructose-1, 6-bisphosphate |
| ADP-HKT Ⅱ | ||
| ADP+D-Glucose | → | AMP+D-Glucose-6-phosphate |
| G6PDH | ||
| D-Glucose-6-phosphate+NADP+ | → | |
| D-Glucono-δ-lactone-6-phosphate+NADPH+H+ | ||
Assay
Principle
-
The assay is based on the decrease in absorbance at 340 nm of NADH in the following reaction
| PFKW Ⅱ | ||
| Fructose–6–P+ATP | → | Fructose–1,6–bisphosphat+ADP |
| PK | ||
| ADP + PEP | → | ATP + Pyruvate |
| LDH | ||
| Pyruvate + NADH + H+ | → | Lactate + NAD+ |
Unit definition
-
One unit is defined as the amount of enzyme which converts 1 μmole of fructose–6–phosphate to Fructose–1,6 – bisphosphate per minute at 37℃ under the conditions specified in the assay procedure.
Reagents
- Reaction mixture (10test)
0.1M Tris–HCl Buffer pH9.0 27.36 ml 0.5M Fructose–6–P solution 0.30 ml 0.1M ATP solution 0.39 ml 56mM PEP solution 0.60 ml 13.1mM NADH solution 0.60 ml 2.5M KCl solution 0.06 ml 0.1M MgSO4 solution 0.60 ml 5,000U/ml PK/
Ammonium sulfate suspension0.03 ml 550U/ml LDH/
Ammonium sulfate suspension0.06 ml - Enzyme dilution buffer
50mM KH2PO4 − NaOH buffer pH8.0 (25℃) - Reagents
-
Tris (hydroxymethyl) aminomethane: Sigma Chemical Co.
#T–1503Fructose–6–phosphate・2Na:FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical CorporationATP (Adenosine triphosphate・2Na・3H2O) :
#066–05341Kyowa Hakko Co.,Ltd.PEP[Phospho (enol) pyruvic acid tr (i cyclohexylammonium)
salt]: Sigma Chemical Co. #P–7252
NADH・ (2Na・3H2O・Reduced form) :Kyowa Hakko Co.,Ltd.PK (Pyruvate kinase) Ammonium sulfate suspension:Roche Diagnostics GmbH. #128163LDH (Lactate dehydrogenase)Ammonium sulfate suspension
Roche Diagnostics GmbH #107085
Enzyme solution
-
Accurately weigh about 10 mg of the sample and add enzyme dilution buffer to make a total of 10 ml. Dilute it with enzyme dilution buffer to adjust the concentration to 5.0–10.0 U/ml.
Procedure
- Pipette accurately 3.0 ml of reaction mixture into a small test tube and preincubate at 30℃.
- After 5 min add accurately 10 μl of enzyme solution and mix to start the reaction at 30℃.
※ In the case of a test blank, add 10 μl of enzyme diluti on buffer in place of enzyme solution. - After starting the reaction, measure the rate of decrease per minutes in absorbance at 340 nm. The rate must be measured within the linear portion of the absorbance curve. (Ex. Linear range from 2 min to 5 min)
-
△A/min = (As/min - Ab/min) ≦ 0.25 Abs/minAbsorbance sample : As/min blank : Ab/min
Calculation
-
Activity (U/mg of powder) = {(△ A/min)/6.22} × 3.01/0.01 × 1/x
= △ A/min. × 48.39 ÷ X6.22 : millimolar extinction coefficient of NADPH at 340nm (cm2/ μmol) 3.01 : final volume (ml) 0.01 : volume of enzyme solution (ml) X : concentration of the sample in enzyme solution ( mg/ml)
Storage
-
Storage at −20℃ in the presence of a desiccant is recommended.
PFKW Ⅱ活性測定法 (Japanese)
試薬液
- 反応試薬混合液 (10 テスト用)
0.1M トリス–HCl 緩衝液 pH9.0 27.36 ml 0.5M フルクトース–6–P 溶液 0.30 ml 0.1M ATP 溶液 0.39 ml 56mM PEP 溶液 0.60 ml 13.1mM NADH 溶液 0.60 ml 2.5M KCl 溶液 0.06 ml 0.1M MgSO4 溶液 0.60 ml 5,000U/ml PK/ 硫安懸濁液 0.03 ml 550U/ml LDH/ 硫安懸濁液 0.06 ml - 酵素溶解用液
50mM KH2PO4–NaOH 緩衝液 pH8.0 (25℃) - 試薬
トリス (ヒドロキシメチル) アミノメタン:シグマ製 #T–1503フルクトース–6– リン酸・2Na:富士フイルム和光純薬製 #066–05341ATP (アデノシン三リン酸・2Na・3H2O) :協和発酵製PEP[ホスホ (エノール) ピルビン酸トリ (シクロヘ
キシルアンモニウム) 塩]:シグマ製 #P–7252
NADH (2Na・3H2O・還元型) :協和発酵製
PK (ピルビン酸キナーゼ) 硫安懸濁液:ロシュ製 #128163LDH (乳酸脱水素酵素) 硫安懸濁液:ロシュ製 #107085
酵素試料液
- 検品約10mg を精密に計り、酵素溶解用液にて溶解し全容10ml とする。その液を更に酵素溶解用液にて5~10U/ml の濃度に適宜希釈する。
測定操作法
- 小試験管に反応試薬混合液3.00ml を正確に分注し、30℃で予備加温する。
- 5 分経過後、酵素試料液10 μl を正確に加え混和し、30℃で反応を開始する。
※ 盲検は酵素試料液の代わりに酵素溶解用液10 μlを加える。
- 反応開始後、340nm における吸光度を測定して直線的に反応している1 分間当たりの吸光度変化を求める。 (直線範囲例:2 分目から5 分目) 求めた吸光度変化を酵素試料液についてはAs/min
盲検液については Ab/min とする。
Δ A/min= (As/min-Ab/min) ≦ 0.25Abs/min
計算
以下の計算式に従い、 PFKW Ⅱ活性 (U/mg) を計算する。活性 (U/mg) = {(△A/min)/(6.22)} × 3.01/0.01 × 1/x
| 6.22 : | NADPH の340nm におけるミリモル分子吸光係数 (cm2 /μmol) |
| 3.01 : | 反応総液量 (ml) |
| 0.01 : | 反応に供した酵素試料液量 (ml) |
| X : | 酵素試料液中の検品濃度 (mg/ml) |
Copyright © Asahi Kasei Pharma Corporation. All rights reserved.