LACTATE OXIDASE [LOXⅡ]
from Aerococcus viridans
(L–Lactate: oxygen oxidoreductase, EC 1.1.3.2)
L–Lactate + O2 → Pyruvate + H2O2
Preparation and Specification
- Appearance
- : Yellowish amorphous powder, lyophilized
- Specific activity
- : More than 20 U/mg solid
- Contaminants
- :
- POP
- Less than 0.001 % (U/U)
- GOD
- Less than 0.001 % (U/U)
- UODN
- Less than 0.001 % (U/U)
- CO
- Less than 0.001 % (U/U)
Properties
- Molecular weight
- : 80 kDa (gel filtration)
- Isoelectric point
- : pH 4.6
- Michaelis constants
- : L–Lactate 7.0 × 10-4M
- Optimum pH
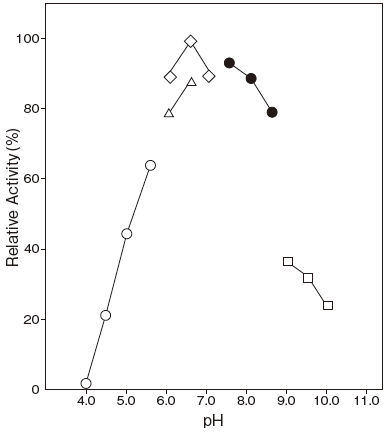
- : 6.0–7.0Figure 1
- pH stability
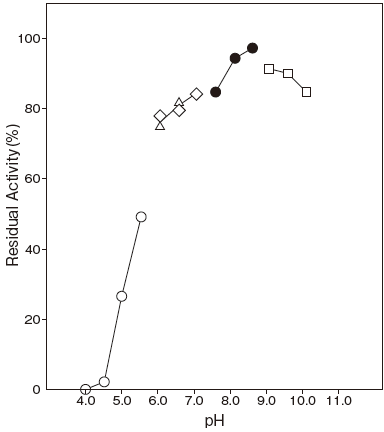
- : 6.0–9.0 (50℃, 10 min) Figure 2
- Optimum temperature
- : 35℃
- Thermal stability
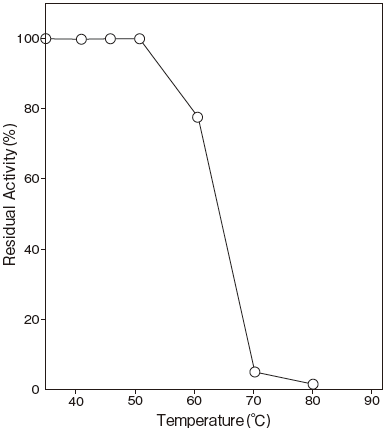
- : Stable at 50℃ and below ( pH 8.5, 10 min) Figure3
- Storage stability
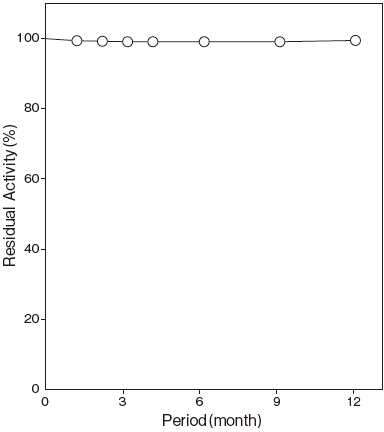
- : At least one year at −20℃Figure4
Applications for Diagnostic Test
This enzyme is useful for enzymatic determination of lactic acid.
| LOX Ⅱ | ||
| L-Lactate + O2 | → | Pyruvate + H2O2 |
| POD | ||
| 2 H2O2 + 4-AA + Phenol | → | Quinoneimine dye + 4 H2O |
Assay
Principle
-
The assay is based on the increase in absorbance at 565 nm as the formation of quinoneimine dye proceeds in the following reactions:
| LOX Ⅱ | ||
| L–Lactate+O2 | → | Pyruvate+H2O2 |
| POD | ||
| 2 H2O2+4–AA+DMA+H+ | → | Quinoneimine dye +4 H2O |
DMA : N, N’–Dimethylaniline
Unit definition
-
One unit is defined as the amount of enzyme which generates 1 μmole of H2O2 per minute at 37℃ under the conditions specified in the assay procedure.
Reagents
- Reaction mixture
0.2 M KH2PO4–NaOH buffer pH 6.5 0.2 ml 50 U/ml POD solution1) 0.1 ml 15 mM 4–AA solution 0.1 ml 0.5 M DL–Lactic acid solution pH 6.5 0.1 ml Distilled water 0.3 ml Mix above reagents in advance. Just before measuring, add the reagent listed below and mix. 0.2% (W/V) DMA solution 0.2 ml 1) : 50 U/ml POD solution
Dissolve 500 U (PPU) of POD with 10 ml of distilled water. - Reaction stopper
0.25% (W/V) LBS solution
LBS: Sodium lauryl sulfate - Enzyme dilution buffer
10 mM KH2PO4 –NaOH buffer pH 7.0 containing
10 μM FAD
FAD: Flavine adenine dinucleotide
- Reagents
DL–Lactic acid:
FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corporation
Special grade #128–00056
DMA: FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corporation
Special grade #044–02763
FAD (2Na) : Kyowa Hakko Co., Ltd.
LBS: NACALAI TESQUE, INC. Extra pure #20123–22
4–AA: NACALAI TESQUE, INC.
Special grade #01907–52
POD: Sigma Chemical Co. Type Ⅱ #P–8250
Enzyme solution
-
Accurately weigh about 20 mg of the sample and add enzyme dilution buffer to make a total of 20 ml. Dilute it with enzyme solution buffer to adjust the concentration as required.
Procedure
- Pipette accurately 1.0 ml of reaction mixture into a small test tube and preincubate at 37℃.
- After 5 min, add exactly 20 μl of enzyme solution and mix to start the reaction at 37℃.
※ In the case of a test blank, add 20 μl of enzyme dilution buffer in place of enzyme solution. - At 10 min after starting the reaction, add 2.0 ml of the reaction stopper to stop the reaction.
- Measure the absorbance at 565 nm.
△A = (As−Ab) ≦ 0.350 AbsAbsorbance sample : As blank : Ab
Calculation
Activity (U/mg of powder) = {(△ A/10)/(35.33×1/2)} × 3.02/0.02 × 1/x| 35.33 : | millimolar extinction coefficient of quinoneimine dye at 565 nm
( cm2 /μmole)
|
| 1/2 : | a multiplier derived from the fact that 2 mole of |
-
H2O2 produces 1 mole of quinoneimine dye 10 : reaction time (min) 3.02 : final volume (ml) 0.02 : volume of enzyme solution (ml) X : concentration of the sample in enzyme solution ( mg/ml)
Storage
Storage at −20℃ in the presence of a desiccant is recommended. The enzyme activity will be retained for at least one year under this condition (Figure 4)
References
- Eichel, H. J. and Rem, L. T. (1962) J. Biol. Chem., 237, 940–945.
- Esders, T. W. and Goodhue, C. T. (1980) Eastman Kodak Company, U. S. Pat. 4,241,178.
LOX Ⅱ活性測定法 (Japanese)
試薬液
- 反応試薬混合液
0.2M KH2PO4–NaOH 緩衝液 pH6.5 0.2 ml 50U/ml POD 溶液 1) 0.1 ml 15mM 4–AA 溶液 0.1 ml 0.5M DL–乳酸溶液 pH6.5 0.1 ml 精製水
を混合して置く。測定直前に前溶液と0.3 ml 0.2% (V/V) DMA 溶液 を混合する。 0.2 ml 1) : 50U/ml POD 溶液
POD 500 単位 (PPU) を精製水10ml で溶解する。 - 反応停止液
0.25% (W/V) LBS 溶液 - 酵素溶解希釈用液
10 μM FAD を含む10mM KH2PO4–NaOH 緩衝液pH7.0 - 試薬
POD:シグマ製 Type Ⅱ #P–8250
4–AA:ナカライテスク製 特級 #01907–52
乳酸 (DL–Lactic acid) :富士フイルム和光純薬製 特級 #128–00056DMA (N,N’–ジメチルアニリン) :
富士フイルム和光純薬製 特級 #044–02763
FAD (フラビンアデニンジヌクレオチド・2Na) :協和発酵製LBS (ラウリルベンゼンスルホン酸ナトリウム) :ナカライテスク製 Extra pure #20123–22
酵素試料液
- 検品約20mg を精密に量り、酵素溶解希釈用液で溶解して全容20ml とする。
その液を酵素溶解希釈用液で適宜希釈する。
測定操作法
- 小試験管に反応試薬混合液1.0ml を正確に分注して37℃で予備加温する。
- 5 分経過後、酵素試料液20 μ1 を加えて混和し、37℃で反応を開始する。
※ 盲検は酵素試料液の代わりに酵素溶解希釈用液20μ1 を加える。 - 10 分経過後、反応停止液2.0ml を加えて混和し、反応を停止する。
- 565nm における吸光度を測定する
求められた吸光度を試料液はAs、盲検液はAb とする。
ΔA = (As−Ab) ≦ 0.350 Abs
計算
- 活性 (U/mg) = {(ΔA/10)/(35.33×1/2)} × 3.02/0.02 × 1/x
-
35.33 : キノンイミン色素の565nm におけるミリモル分子吸光係数 (cm2 / μmole)1/2 : H2O2 2 モルからキノン色素1 モルが生成することによる係数 10 : 反応時間 (min) 3.02 : 反応総液量 (ml) 0.02 : 反応に供した酵素試料液量 (ml) X : 酵素試料液中の検品濃度 (mg/ml)
Copyright © Asahi Kasei Pharma Corporation. All rights reserved.