CHOLINE OXIDASE [COD]
from Arthrobacter globiformis
(Choline: oxygen 1-oxidoreductase, EC 1.1.3.17)
Choline + O2 → Betaine aldehyde + H2O2
Betaine aldehyde + O2 + H2O → Betaine + H2O2
Preparation and Specification
- Appearance
- : Yellowish amorphous powder, lyophilized
- Specific activity
- : More than 8 U/mg solid
- Contaminants
- : CatalaseLess than 10.0 % (U/U)
- : Glucose oxidaseLess than 0.01 % (U/U)
Properties
- Substrate specificity
- : See Table 1
- Molecular weight
- : 83 kDa (Sephadex G–150)
- Isoelectric point
- : pH 4.5
- Michaelis constants
- : Choline 1.2 × 10-3M
Betaine aldehyde 8.7 × 10-3M
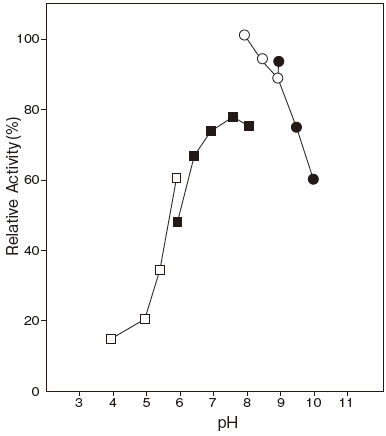
- Optimum pH
- : 7.5–8.0Figure 1
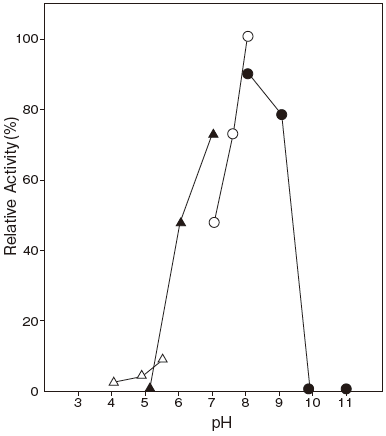
- pH stability
- : 7.5–9.0 (37℃, 10 min) Figure 2
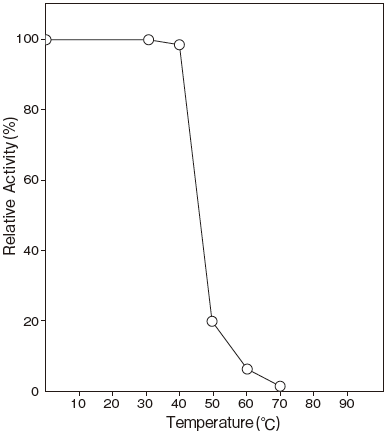
- Thermal stability
- : Stable at 40℃ and below (pH 7.5, 10 min) Figure3
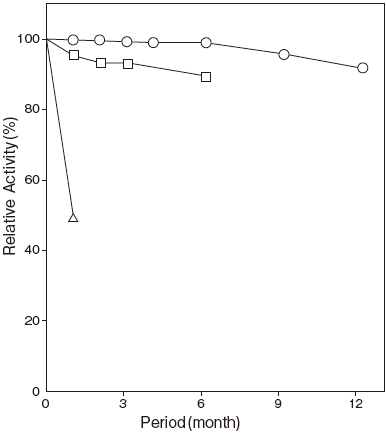
- Storage stability
- : At least one year at –20℃Figure4
- Effect of various
chemicals - : See Table 2
Applications for Diagnostic Test
This enzyme is useful for enzymatic determination of phospholipids coupled with phospholipase D (T–07) .
| PLD | ||
| Phosphatidylcholine + H2O | → | Choline + Phosphatidic acid |
| COD | ||
| Choline + 2 O2 + H2O | → | Betaine + 2 H2O2 |
| POD | ||
| 2 H2O2 + 4-AA + Phenol | → | Quinoneimine dye + 4 H2O |
Table 1. Substrate specificity
| Substrate | Relative activity (%) |
|---|---|
| Choline | 100 |
| Betaine aldehyde | 46 |
| Diethanolamine | 1 |
| Triethanolamine | 3 |
| N, N-Dimethylaminoethanol | 5 |
| N-Methylethanolamine | 0 |
Table 2. Effect of various chemicals on COD activity
| Additives | Consentration | Relative activity (%) |
|---|---|---|
| None | – | 100 |
| Triton X-100 | 0.1% | 96 |
| Adekatol SO-120 | 0.1% | 106 |
| Sodium laurylsulfate | 0.1% | 94 |
| Deoxycholate | 0.1% | 94 |
| Sodium laurylbenzene sulfate | 0.1% | 91 |
| CaCl2 | 5mM | 101 |
| MgCl2 | 5mM | 100 |
| FeCl3 | 5mM | 0 |
| ZnCl2 | 5mM | 8 |
| MnCl2 | 5mM | 98 |
| CoCl2 | 5mM | 31 |
| MoCl2 | 5mM | 58 |
| KCl | 5mM | 93 |
| NaCl | 5mM | 97 |
| NH4Cl | 5mM | 100 |
| LiCl | 5mM | 97 |
| BaCl2 | 5mM | 103 |
Assay
Principle
-
The assay is based on the increase in absorbance at 500 nm as the formation of quinoneimine dye proceeds in the following reactions:
| COD | ||
| Choline+O2 | → | Betaine aldehyde+H2O2 |
| COD | ||
| Betaine aldehyde+O2+H2O | → | Betaine+H2O2 |
| POD | ||
| 2 H2O2+4-AA+Phenol | → | Quinoneimine dye+4 H2O |
Unit definition
-
One unit is defined as the amount of enzyme which generates 1 μmole of H2O2 per minute at 37℃ under the conditions specified in the assay procedure.
Reagents
- Reaction mixture
1.211 g of Tris (hydroxymethyl) amino methane, 2.1 g of choline chloride and 2 ml of 1 % (W/V) phenol are dissolved with 1 N HCl and adjusted to pH 8.0 (25℃) . Then, 1 ml of 1 % (W/V) 4–AA and 3 ml of 100 PPU/ ml POD are added to make a total of 100 ml. - Enzyme dilution buffer
10 mM Tris–HCl buffer (pH 8.) containing 2 mM
EDTA: Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid - Reagents
Choline chloride:
FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corporation4-AA: NACALAI TESQUE, INC. Special grade #01907–52
1st Grade #033–09812
POD: Sigma Chemical Co. Type Ⅱ #P–8250
EDTA (2 Na・2H2O) : KISHIDA CHEMICAL Co., Ltd.#060–29133
Enzyme solution
-
Accurately weigh about 20 mg of the sample and add enzyme dilution buffer to make a total of 20ml.
Dilute it with enzyme dilution buffer to adjust the concentration as required.
Procedure
- Pipette accurately 1.90 ml of reaction mixture into a small test tube and preincubate at 37℃.
- After 5 min, add 50 μl of enzyme solution and mix to start the reaction at 37℃.
- After starting the reaction, measure the rate of increase per minute in absorbance at 500 nm. The rate must be measured within the linear portion of the absorbance curve.
Calculation
- Activity (U/mg of powder) = {(△ A/min)/(12.0×1/2)} × 3.05/0.05 × 1/x
12.0 : millimolar extinction coefficient of quinoneimine dye at 500 nm (cm2/μmole)
-
1/2 : multiplier derived from the fact that 2 mole of H2O2 produce 1 mole of quinoneimine dye. 3.05 : final volume (ml) 0.05 : volume of enzyme solution (ml) X : concentration of the sample in enzyme solution ( mg/ml)
Storage
-
Storage at –20℃ in the presence of a desiccant is recommended. Enzyme activity will be retained for at least one year under this condition (Figure 4)
References
- Ikuta, S., Matsuura, K., Imamura, S., Misaki, H. and Horiuchi, Y. (1977) J. Biochem., 82, 157–163.
- Ikuta, S., Imamura, S., Misaki, H. and Horiuchi, Y. (1977) ibid, 82, 1741–1749.
- Ohta–Fukuyama, M., Miyake, Y., Emi, S. and Yamano, T. (1989) J. Biochem., 88, 197–203.
- Takayama, M. et al. (1977) Clin. Chim. Acta, 79, 93.
- Sugawara, K. and Kihara, A. (1978) Eisei Kensa, 27 (1) , 106–111.
- Okabe, H. et al. (1977) Clin. Chim. Acta, 80, 87.
COD 活性測定法 (Japanese)
試薬液
- 反応試薬混合液
トリス (ヒドロキシメチル) アミノメタン1.211gと塩化コリン2.1g 及び1% (W/V) フェノール液2ml を精製水に溶解した後、1N HCl でpH8.0 (25℃) に調整し、さらに1% (W/V) 4–AA 溶液1ml と100PPU/ml POD 溶液3ml を加えて溶かし、全容100ml とする。 - 酵素溶解希釈用液
2mM EDTA と1% (W/V) KCl を含む10mM トリス- HCl 緩衝液pH8.0 溶液
酵素溶解希釈用液
50mM トリス−HCl 緩衝液 pH9.0 - 試薬
塩化コリン:富士フイルム和光純薬製 一級#033–098124-AA:ナカライテスク製 特級 #01907–52
POD:シグマ製 Type Ⅱ #P–8250
EDTA (エチレンジアミン四酢酸・2Na・2H2O) :キシダ化学製 #060–29133
酵素試料液
- 検品約20mg を精密に量り、酵素溶解希釈用液で溶解して全容20ml とする。
その液を酵素溶解希釈用液で適宜希釈する。
測定操作法
- 小試験管に反応試薬混合液3.0ml を正確に分注し37℃で予備加温する。
- 5 分経過後、酵素試料液50 μl を正確に加えて混和し、37℃で反応を開始する。
- 反応開始後、500nm における吸光度を測定して直線的に反応している1 分間当たりの吸光度変化を求める。
ΔA/min ≦ 0.040 Abs/min
計算
活性 (U/mg) = {(△ A/min)/(12.0×1/2)} × 3.05/0.05 × 1/x| 12.0 : | キノンイミン色素の500nm におけるミリモル分子吸光係数 (cm2/ μmole) |
| 1/2 : | H2O2 2 モルからキノンイミン色素1 モルが生成することによる係数 |
| 3.05 : | 反応総液量 (ml) |
| 0.05 : | 反応に供した酵素試料液量 (ml) |
| X : | 酵素試料液の検品濃度 (mg/ml) |