Preparation and Specification
- Appearance
- : White to brownish amorphous powder, lyophilized
- Specific activity
- : More than 30 U/mg solid
Properties
- Molecular weight
- : 20 kDa (Sephadex G–100)
- Isoelectric point
- : pH 7.0
- Michaelis constants
- : Phosphatidylcholine 2.0 × 10-2M
- Optimum pH
- : 7.0–9.0Figure 1
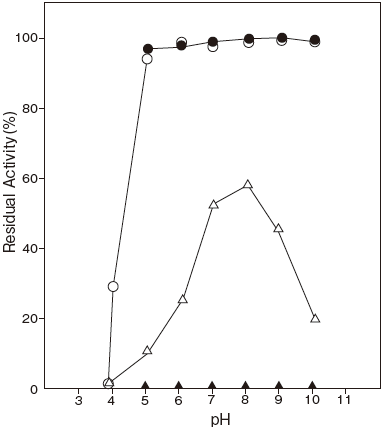
- pH stability
- : 5.0–10.0 (in 0.1% BSA) Figure 2
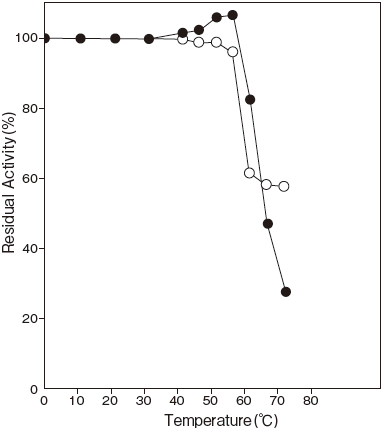
- Thermal stability
- : Stable at 55℃ and below ( pH 7.5, 10 min) Figure3
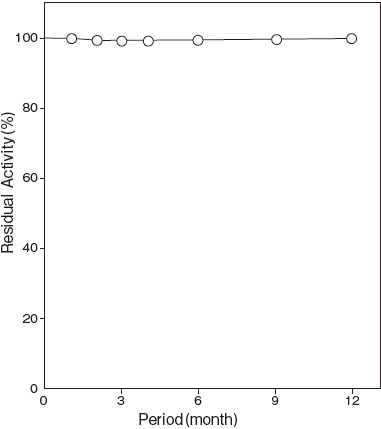
- Storage stability
- : At least one year at -20℃Figure4
- Effect of various chemicals
- : See Table 1 and Table 2
- Activator
- : Ca2+, Sodium deoxycholate
- Inhibitor
- : Tris–HCl buffer
Applications for Diagnostic Test
This enzyme is useful for enzymatic determination of lecithin when coupled with alkaline phosphatase (T–08) and choline oxidase (T–05) .
| PLC | ||
| Lecithin + H2O | → | Phosphorylcholine + Diglyceride |
| ALP | ||
| Phosphorylcholine + H2O | → | Choline + Pi |
| COD | ||
| Choline + 2 O2 + H2O | → | Betaine + 2 H2O2 |
| POD | ||
| 2 H2O2 + 4-AA + Phenol | → | Quinoneimine dye + 4 H2O |
Table 1. Effect of detergents on PLC activity
| Detergent | Concentration (%) |
Relative activity (%) |
|---|---|---|
| None |
0 |
100 |
| Triton X–100 |
0.1 |
43 |
| Adekatol SO–120 |
0.1 |
63 |
| Deoxycholate |
0.1 |
248 |
| Tween 20 | 0.1 | 16 |
Table 2. Effect of metal ions on PLC activity
| Metal ion | Concentration (mM) |
Relative activity (%) |
|---|---|---|
| None |
0 |
100 |
| NaCl |
100 |
103 |
| KCl |
100 |
102 |
| CaCl2 | 10 |
128 |
| MgCl2 | 10 |
123 |
| CoCl2 | 10 |
33 |
| MnCl2 | 10 |
54 |
| ZnCl2 | 10 |
79 |
| BaCl2 | 10 |
91 |
| EDTA | 10 | 26 |
Fig.1 pH Optimum
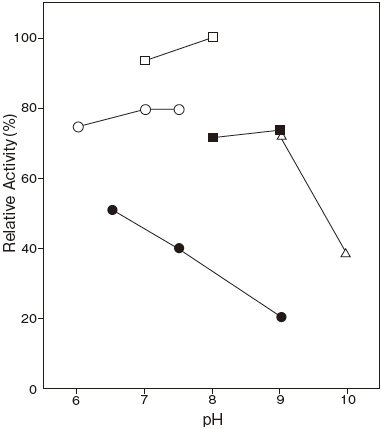
●: Tris-HCI buffer
□: Collidine buffer
■: Diethanolamine-HCI buffer
△: Glycine-NaOH buffer
Assay
Principle
-
The assay is based on the increase in absorbance at 500 nm as the formation of quinoneimine dye proceeds in the following reactions:
| PLC | ||
| Phosphatidyl choline+H2O | → | 1, 2–Diglyceride+Phosphoryl choline |
| ALP | ||
| Phosphoryl choline+H2O | → | Choline+Orthophosphate |
| COD | ||
| Choline+2 O2+H2O | → | Betaine+2 H2O2 |
| POD | ||
| 2 H2O2+Phenol+4–AA | → | Quinoneimine dye+4 H2O |
ALP: Alkaline phosphatase
COD: Choline oxidase
Unit definition
One unit is defined as the amount of enzyme which
- liberates 1 μmole of phosphoryl choline per minute at 37℃ under the conditions specified in the assay procedure.
Reagents
- Reaction mixture for the first reaction
0.2 M DMG–NaOH buffer pH 7.5 0.20 ml 10 mM Egg lecithin solution 1) 0.20 ml Distilled water 0.50 ml DMG: 3, 3–Dimethylglutarate 1) : 10 mM Egg lecithin solution
Pour the entire contents of one ampoule of egg lecithin into a test tube and remove ether. Then dry contents under reduced air pressure with rotary evaporator. Accurately weigh 1 g of egg lecithin into a beaker and add 135 ml of 0.5% deoxycholate (DOC) ※) solution to dried product and suspend in homogenizer.※) : 0.5% DOC solution Suspend 250 mg of deoxycholic acid with 40 ml of distilled water, adjust pH to 8.0 with 4 N NaOH, and add distilled water to make a total of 50 ml.
- Reagent mixture for the second reaction
15 mM 4–AA solution 0.10 ml 0.2% (W/V) Phenol 0.10 ml 50 mM Tris–HCl buffer, pH 8.0 0.50 ml 90 U/ml POD 2) 0.10 ml 30 U/ml COD 3) 0.10 ml 80 U/ml ALP 4) 0.10 ml 2) : 90 U/ml POD
Dissolve 900 U (PPU) of POD with 10 ml of distilled water.3) : 30 U/ml COD
Dissolve 300 U of COD with 10 ml of 10 mM Tris–HCl buffer (containing 1% KCl) , pH 8.0.4) : 80 U/ml ALP
Dissolve 800 U of ALP with 10 ml of 10 mM Tris–HCl buffer pH 9.0. - Reaction stopper
1 M Tris–HCl buffer pH 8.0 containing 0.2% (W/V) sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) - Enzyme dilution buffer
10 mM DMG–NaOH buffer, pH 7.5 containing 0.1% (W/V) BSA - Reagents:
DMG: Tokyo Kasei Kogyo Co. Ltd. #D1322
Egg lecithin: Sigma Chemical Co. Type X VI –E #P–3556–1G
DOC: NACALAI TESQUE, INC. # 107–11
COD: Asahi Kasei Pharma Corporation # T–05
ALP: Asahi Kasei Pharma Corporation # T–08
4–AA: NACALAI TESQUE, INC. Special grade # 01907–52
POD : Sigma Chemical Co. Type II #P–8250
Enzyme solution
-
Weigh about 20 mg of test sample exactly and add enzyme dilution buffer to make a total of 20 ml. Dilute it with enzyme dilution buffer as required.
Procedure
- Pipette 0.90 ml of reagent mixture for the first reaction into a small test tube and preincubate at 37℃.
- After 5 min, add exactly 100 μl of enzyme sample and mix to start the first reaction at 37℃.
※ In the case of a test blank, add 100 μl of enzyme
-
dilution buffer in place of enzyme solution. - After 10 min, add 1.0 ml of reaction stopper and mix.
On stopping the first reaction, add 1.0 ml of the reaction mixture for the second reaction immediately to start the second reaction at 37℃. - After 20 min, measure the absorbance at 500 nm.
△A = (As−Ab) ≦ 0.30 AbsAbsorbance sample : As blank : Ab
Calculation
- Activity (U/mg) = {(△A/10)/(12.0)} × 3.00/0.10 × 1/x
-
12.0 : millimolar extinction coefficient of quinoneimine dye at 500 nm (cm2/ μmole) 10 : reaction time (min) 3.0 : final volume (ml) 0.10 : volume of enzyme solution (ml) X : concentration of the sample in enzyme solution ( mg/ml)
Storage
-
Storage at -20℃ in the presence of a desiccant is recommended. Enzyme activity will be retained for at least one year under this condition (Figure 4)
References
- Zwaal, R. F., Roelofsen, B., Comfurius, P.S. and Van
Deenen , L. L. M (. 1971) Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 233, 474. - Otnaess, A. B., Prydz, H., Bjoerklid, E. and Berre, A. (1972) Eur. J. Biochem., 27, 238.
PLC 活性測定法 (Japanese)
試薬液
- 第一反応試薬混合液
0.2M DMG–NaOH 緩衝液 pH7.5 0.20 ml 10mM 卵黄レシチン溶液1) 0.20 ml 精製水 0.50 ml 1) : 10mM 卵黄レシチン溶液
卵黄レシチン1 g をビーカーに量りとり、0.5%DOC 溶液※) 135ml を加えてホモジナイザーにより分散懸濁する。※) : 0.5%DOC 溶液
デオキシコール酸250mg を精製水40mlに懸濁して4N NaOH を加えpH8.0 位にして溶解した後、精製水で全容50ml とする。
- 第二反応試薬混合液
15mM 4–AA 溶液 0.10 ml 0.2% (W/V) フェノール液 0.10 ml 30U/ml COD 溶液2) 0.10 ml 90U/ml POD 溶液3) 0.10 ml 80U/ml ALP 溶液4) 0.10 ml 50mM トリス–HCl 緩衝液pH8.0 0.50 ml 2) : 30U/ml COD 溶液
COD 300 単位 (U) を1% KCl を含む10mM トリス–HCl 緩衝液pH8.0 10ml で溶解する。3) : 90U/ml POD 溶液
POD 900 単位 (PPU) を精製水10ml 溶解する。4) : 80U/ml ALP 溶液
ALP 800 単位 (U) を10mM トリス–HCl 緩衝液pH9.0 10ml で溶解する。
- 反応停止液
0.2% (W/V) ドデシル硫酸ナトリウム (SDS) を含む1M トリス–HCl 緩衝液pH8.0 - 酵素溶解希釈用液
0.1% (W/V) BSA を含む10mM DMG–NaOH 緩衝液pH7.5 - 試薬
DMG (3,3–ジメチルグルタル酸) :東京化成製 #D1322卵黄レシチン (L–α–フォスファチジルコリン) :
シグマ製Type X VI–E #P–3556–1G
DOC (デオキシコール酸) :ナカライテスク製#107–11COD (コリン酸化酵素) :旭化成ファーマ製 #T–05
ALP (アルカリフォスファターゼ) :旭化成ファーマ製 #T–084–AA:ナカライテスク製 特級 #01907–52
POD:シグマ製 Type Ⅱ #P–8250
酵素試料液
- 検品約20mg を精密に量り、酵素溶解希釈用液で全容20ml とする。
その液を酵素溶解希釈用液で適宜希釈する。
測定操作法
- 小試験管に第一反応試薬混合液0.90ml を正確に分注し、37℃で予備加温する。
- 5 分経過後、酵素試料液100 μl を正確に加えて混和し、37℃で第一反応を開始する。
※ 盲検は酵素試料液の代わりに酵素溶解希釈用液100μl を加える。 - 10 分経過後、反応停止液1.0ml を加えて混和後、直ちに第二反応試薬混合液1.0ml を加えて混和し、37℃で第二反応を開始する。
- 20 分経過後、500nm における吸光度を測定する。求められた吸光度を試料液はAs、盲検液はAb とする。
ΔA = ( As-Ab) ≦ 0.30 Abs
計算
活性 (U/mg) = {(ΔA/10)/(12.0)} × 3.00/0.10 × 1/x| 12.0 : | キノンイミン色素の500nm におけるミリモル分子吸光係数 (cm2 / μmole) |
| 10 : | 反応時間 (min) |
| 3.00 : | 反応総液量 (ml) |
| 0.10 : | 反応に供した酵素試料液量 (ml) |
| X : | 酵素試料液中の検品濃度 (mg/ml) |