ASCORBATE OXIDASE [ASOK]
from Microorganism
(L‒Ascorbate: oxygen oxidoreductase, EC 1.10.3.3)
L‒ Ascorbic Acid + 1/2 O2 → Dehydroascorbic Acid + H2O
Preparation and Specification
- Appearance
- : Light blue to blue lyophilizate
- Specific activity
- : More than 200 U/mg solid
Properties
- Substrate specificity
- : See Table 1
- Molecular weight
- : 80 kDa (gel filtration)
- Isoelectric point
- : pH 4.0
- Michaelis constants
- : Ascorbic acid (pH 7.0) 1.0 × 10-4 M
Ascorbic acid (pH 4.0) 3.8 × 10-4 M
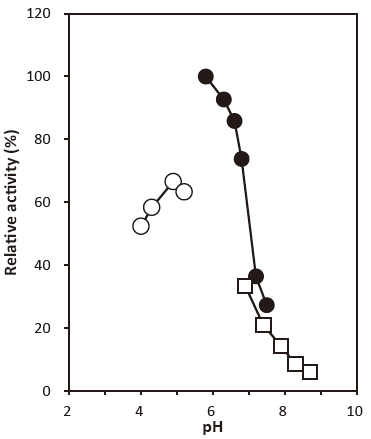
- Optimum pH
- : 4.0–4.5 (Acetate buffer) Figure 1
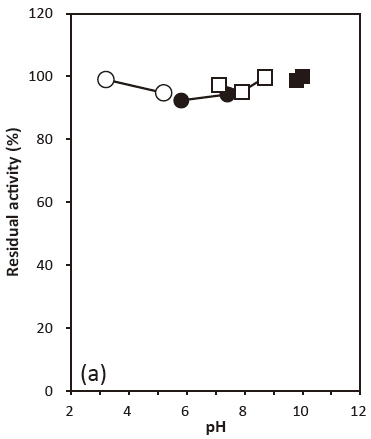
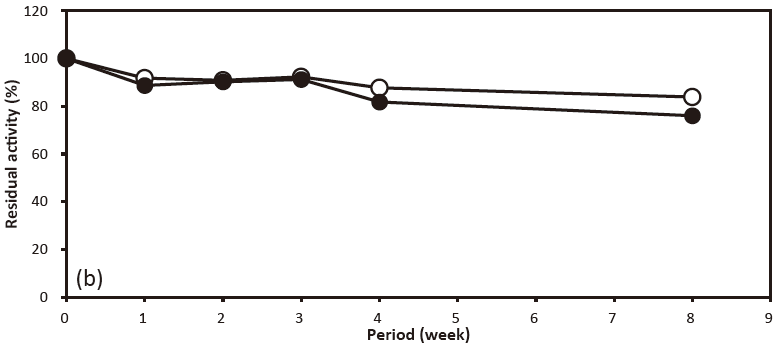
- pH stability
- : 6.0–9.0 (30℃, 24 hr) Figure 2
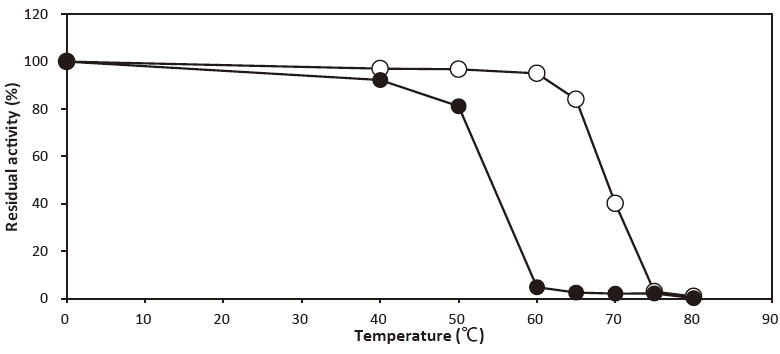
- Thermal stability
- : Stable at 50℃ and below (pH 7.0, 10 min) Figure 3
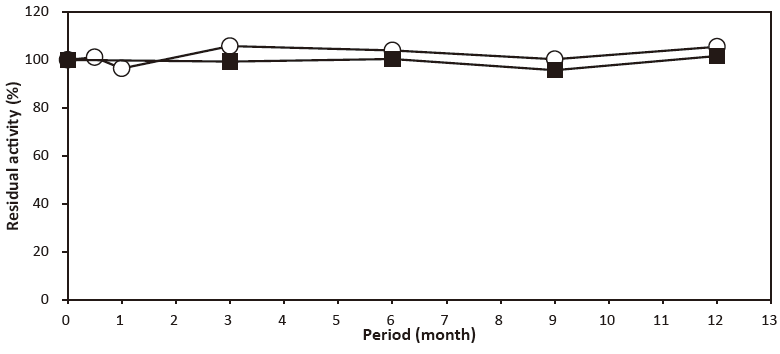
- Liquid stability
- : See Figure 4
- Effect of metal ions
- : See Table 2
- Stabilizers
- : BSA, Mannitol
Properties
- Molecular weight
- : 8 kDa(SDS-PAGE)
- Isoelectric point
- : 5.1 (estimated from amino acid sequence)
- Michaelis constant
- : 4.3 × 10-4M
- Optimum pH
- : 5.8‒6.3Figure 1
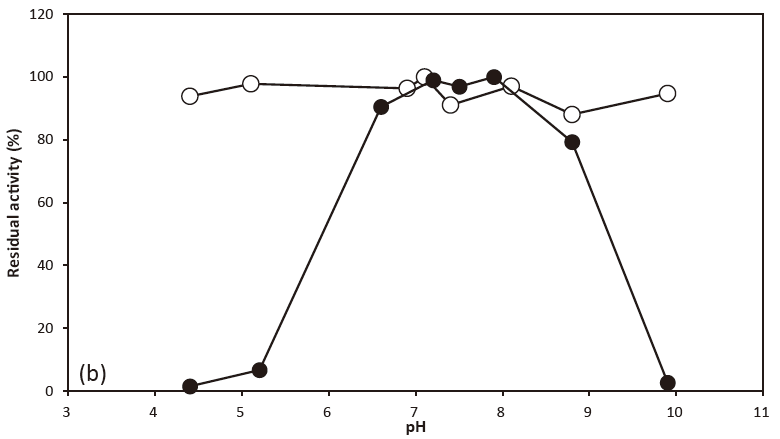
- pH stability
- : 3.2‒10.0(30℃, 24 hr)Figure 2
- Thermal stability
- : Stable at 60℃ and below(pH 7.0, 10 min)Figure 3
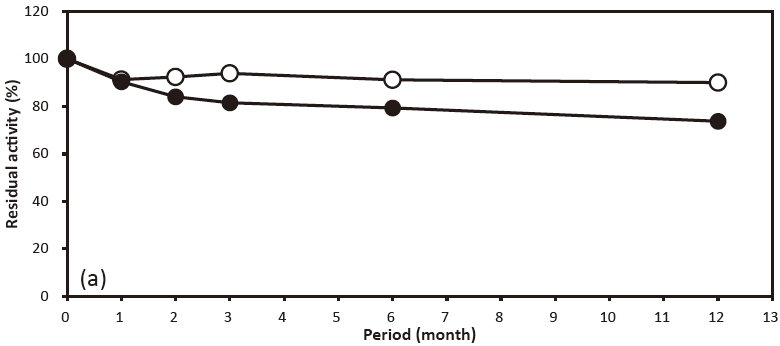
- Storage stability
- : Stable at least one year at -20℃Figure 4
- Solid stability
- : See Figure 5
- Effect of metal ions
- : See Table 1
- Effect of detergents
- : See Table 2
- Light stability
- : See Table 3
- Stabilizers
- : BSA, Mannitol, Trehalose
Applications for Diagnostic Test
This enzyme is useful for avoidance from interference of ascorbic acid on diagnostic assay such as blood, uric acid, TG, TC and creatinine.
Table 1 Effect of metal ions on ASOK activity
| Metal ion (1 mM) | Relative activity (%) |
|---|---|
| None | 100 |
| MgCl2 | 97 |
| MgSO4 | 98 |
| ZnCl2 | 95 |
| ZnSO4 | 100 |
| NaCl | 97 |
| NH4Cl | 96 |
| BaCl2 | 96 |
| NiCl2 | 95 |
| CoCl2 | 96 |
| MnCl2 | 99 |
| LiCl2 | 96 |
| KCl | 97 |
| CaCl2 | 99 |
| FeCl2 | 97 |
Table 2 Effect of detergents on ASOK stability
| Detergent (0.1%) | Residual activity (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 0℃ | 65℃ | 70℃ | |
| None (0.1% BSA) | 100 | 71 | 28 |
| TritonX-100 | 100 | 81 | 41 |
| Emulgen 1108 | 100 | 81 | 40 |
| Emulgen 1118S-70 | 100 | 85 | 42 |
| Emulgen 1150S-60 | 100 | 81 | 41 |
| Adekatol TN-100 | 100 | 84 | 42 |
| Newcol 710 | 100 | 83 | 45 |
| Newcol 710-F | 100 | 83 | 46 |
| Newcol 714-F | 100 | 85 | 44 |
| Newcol 707 | 100 | 87 | 47 |
After 10 min of incubation at each temperature.
Table 3 Light stability
| Light source | Residual activity (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| 0h | 24h | |
| LED | 100 | 102 |
| Fluorescent | 100 | 101 |
| UV | 100 | 74 |
After 24 hours of incubation.
Assay
Principle
-
The assay is based on the decrease in absorbance at 245 nm as ascorbic acid is oxidized in the following reaction:
| ASOK | ||
| Ascorbic acid+1/2 O2 | → | Dehydroascorbic acid+H2O |
Unit definition
-
One unit is defined as the amount of enzyme which oxidizes 1 μmole of ascorbate to dehydroascorbate per minute at 30 ℃ under the conditions specified in the assay procedure.
Reagents
- Reaction mixture
Dilute substrate solution for stock 1) with dilution buffer 2)
to make a 20‒fold solution.1): Substrate solution for stock(10 mM L‒ascorbic acid solution)
Dissolve 176 mg of L‒ascorbic acid and 37 mg of EDTA with 100 ml of 1mM HCl.
EDTA: Ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid2): Dilution buffer
90mM KH2PO4‒5mM Na2HPO4 buffer containing 0.45 mM EDTA - Reaction stopper
0.2 N HCl solution - Enzyme dilution buffer
10 mM Na2HPO4 solution containing 0.05%(W/V)BSA - Reagents
L‒Ascorbic acid:
FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corporation
Special grade # 012‒04802
EDTA(2Na・2H2O): KISHIDA CHEMICAL Co., Ltd.
#060‒29133
BSA: Millipore Fraction V pH 5.2 #81‒053
Enzyme solution
-
Accurately weigh about 20 mg of the sample and add enzyme dilution buffer to make a total of 20 ml. Dilute it with enzyme dilution buffer to adjust the concentration to within 0.08‒0.35 U/ml.
Procedure
- Pipette accurately 1.0 ml of reaction mixture into a small test tube and preincubate at 30℃.
- After 5 min, add exactly 100 μl of enzyme solution and mix to start the reaction at 30℃.
- At 5 min after starting the reaction, add 3.0 ml of the reaction stopper to stop the reaction.
※ In the case of a test blank, add 100 μl of enzyme dilution buffer after adding reaction stopper in place of enzyme solution. - Measure the absorbance at 245 nm.
-
0.100Abs ≦ ΔA = Ab-As ≦ 0.420AbsAbsorbance sample : As blank : Ab
Calculation
-
Activity(U/mg of powder)= {(△A/5)/(10.0)} × 4.10/0.10 × 1/x
10.0 : millimolar extinction coefficient of ascorbic acid at 245 nm at pH 1.0(cm2/ μmole) 5 : reaction time(min) 4.10 : final volume(ml) 0.10 : volume of enzyme solution(ml) X : concentration of the sample in enzyme solution ( mg/ml)
Storage
-
Storage at -20℃ in the presence of a desiccant is recommended.
References
- Murao, S., et al. (1991) Agric. Biol. Chem., 55(6), 1693‒1694.
- Nakamura, T., Makino, N. and Ogura, Y. (1968) J. Biochem., 64, 189.
- Aikazyan, V. Ts. and Nalbandyan, R. M.(1979)FEBS Lett, 104, 127.
- White, G. A. and Smith, F. G. (1961) Nature, 190, 187.
ASOK 活性測定法(Japanese)
試薬液
- 保存基質溶液(10mM L‒アスコルビン酸)
L‒アスコルビン酸 176mg とEDTA 37mg を1mM
HCl 100ml で溶解する。 - 反応試薬混合液
上記の保存基質溶液を希釈用液※)で20 倍に希釈する。※): 希釈用液
0.45mM EDTA を含む90mM KH2PO4‒5mM
Na2HPO4 溶液 - 反応停止液
0.2N HCl 液 - 4.酵素溶解希釈用液
0.05%(W/V)BSA を含む10mM Na2HPO4 溶液 - 試薬
L‒アスコルビン酸:富士フイルム和光純薬製 特級 #012‒04802EDTA(エチレンジアミン四酢酸・2Na・2H2O):キシダ化学製 #060‒29133BSA: Millipore 社製 Fraction V pH5.2 #81‒053
酵素試料液
- 検品約20mg を精密に量り、酵素溶解希釈用液に溶解して全容20ml とする。
その液を酵素溶解希釈用液で0.08~0.35U/ml 濃度となるように適宜希釈する。
測定操作法
- 小試験管に反応試薬混合液1.0ml を正確に分注して30℃で予備加温する。
- 5 分経過後、酵素試料液100 μl を加えて混和し、30℃で反応を開始する。
- 5 分経過後、反応停止液3.0ml を加えて混和し、反応を停止する。
※ 盲検は反応停止後に酵素試料液100 μl を加える。 - 245nm における吸光度を測定する。
求められた吸光度を試料液はAs、盲検液はAb とする。
0.100Abs ≦ ΔA = Ab-As ≦ 0.420Abs
計算
活性(U/mg)= {(ΔA/5)/(10.0)} × 4.10/0.10 × 1/x| 10.0 : | pH 1 の条件でアスコルビン酸の245nm におけるミリモル分子吸光係数 (cm2 /μmole) |
| 5 : | 反応時間(min) |
| 4.10 : | 反応総液量(ml) |
| 0.10 : | 反応に供した酵素試料液量(ml) |
| X : | 酵素試料液中の検品濃度(mg/ml) |