LIPASE [LPM]
mixture of LP (T–01) and MGLP II (T–117)
Triglyceride + 3 H2O → Glycerol + 3 Fatty Acid
| ★ | Advantages | |
| ① | High Reactivity | |
| ② | Thermal stability | |
| ③ | Stability in solution | |
Preparation and Specification
- Appearance
- : White to pale brownish amorphous powder, lyophilized
- Specific activity
- : LP ; 1500–3500 U/mg
Applications for Diagnostic Test
The enzyme is useful for enzymatic determination of triglyceride when
| LPM | ||
| TG + 3H2O | → | Glycerol + 3 FFA |
| GKZ | ||
| Glycerol + ATP | → | G-3-P + ADP |
| GPOSP | ||
| G-3-P + O2 | → | DHAP + H2O2 |
| POD | ||
| 2H2O2 + 4-AA + Phenol | → | Quinoneimine dye + 4 H2O |
TG : Triglyceride
FFA : Free fatty acid
DHAP : Dihydroxyacetone phosphate
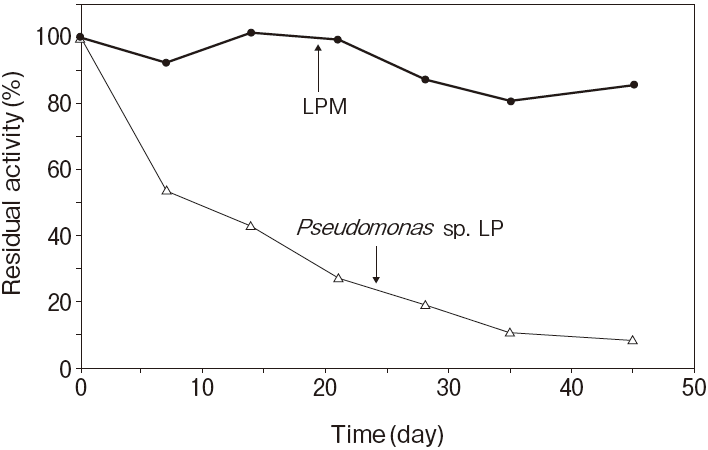
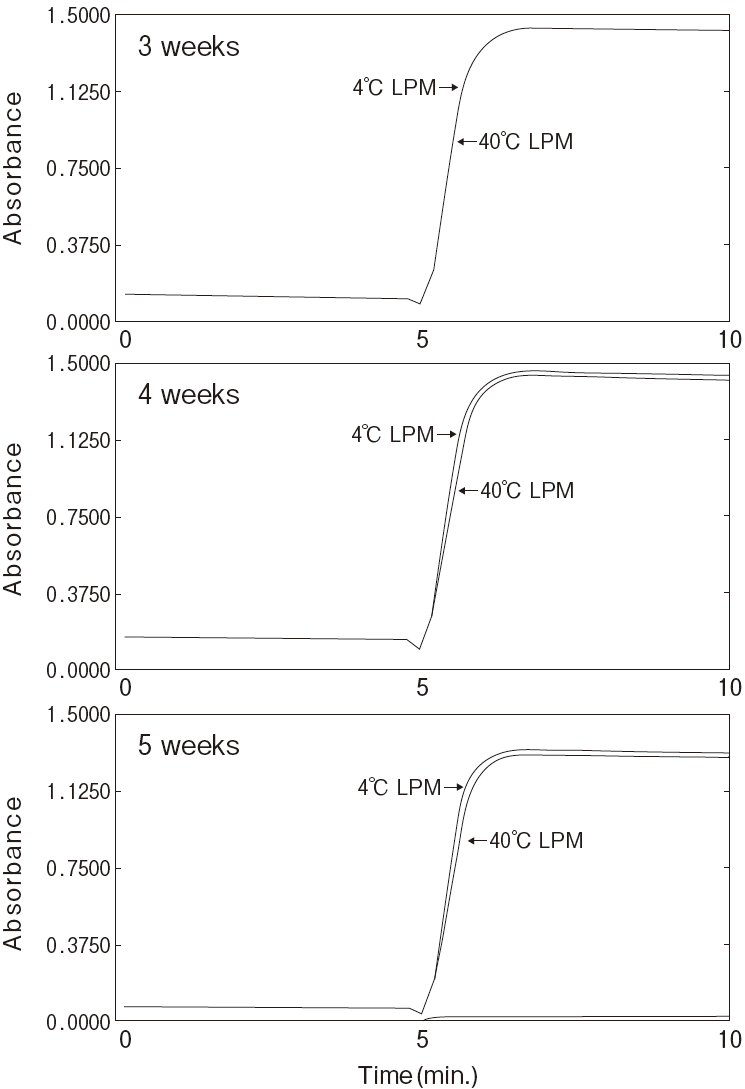
Fig.1 Thermal stability
Stored in R2 of TG reagentResidual activity (%) after 30 min. at each temperature
Activity assay method: 37℃
Titration method using olive oil as substrate
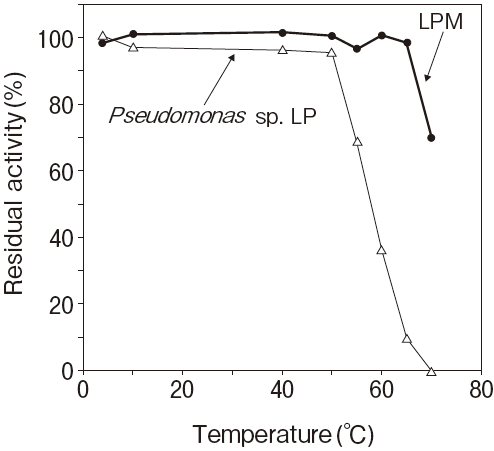
Pseudomonas sp. LP : 50℃ 30 min.
20mM, PIPES pH7
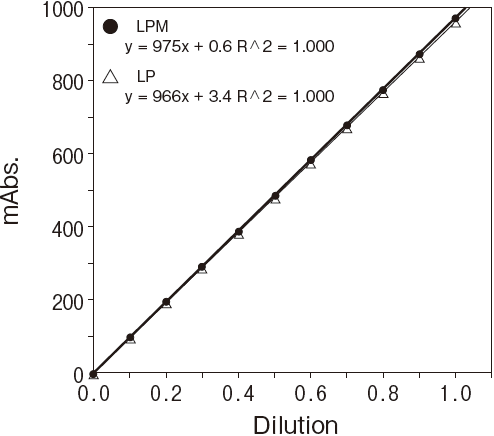
Fig.2-1 Dilution linearity using human serum
Sample : Human serumAnalyzer : Hitachi 7150
Reaction time course
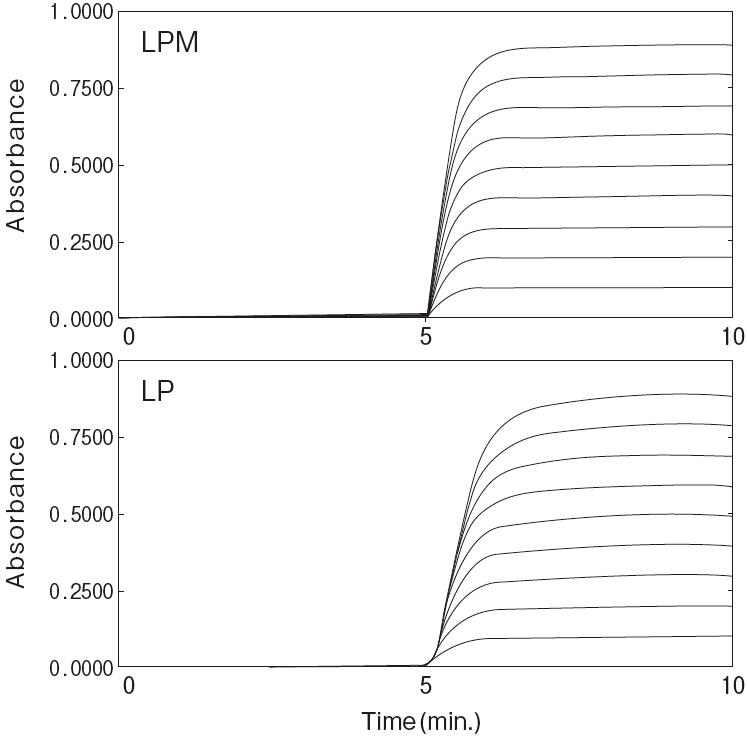
Fig.2-2 Dilution linearity using human serum
Sample : Human serumAnalyzer : Hitachi 7150
Linearity in dilution
Assay
Principle
The assay is based on the titration of fatty acids liberated in the following reactions:
| LPM | ||
| Triglyceride+3 H2O | → | Glycerol+3 Fatty acid |
| ( Titration) | ||
| Fatty acid+NaOH | → | Na–Fatty acid+H2O |
Unit definition
-
One unit is defined as the amount of enzyme which liberates 1 μmole of fatty acid per minute at 37℃ under the conditions specified in the assay procedure.
Reagents
- Substrate suspension (Olive oil and Adekatol SO–120) 50 g of Olive oil: (Japanese Pharmacopoeia grade) and 50 g of Adekatol SO–120 are suspended with 150 ml of distilled water.
- Reaction stopper
Mixture of ethanol and acetone (1:1) - Indicator
1% (W/V) Phenolphthalein–ethanol solution - Titration solution
50 mM NaOH solution - Enzyme dilution buffer
0.1 M KH2PO4–NaOH buffer, pH 8.0 containing
0.1% (W/V) BSA and 0.1% (W/V) NaN3 - Reagents
Olive oil: (Japanese Pharmacopoeia grade)
Ethanol: (Japanese Pharmacopoeia grade)
Adekatol SO–120: ADEKA CORPORATION
BSA: Millipore Fraction V pH5.2 #81–053
Enzyme solution
-
Accurately weigh about 10 mg of the sample and add enzyme dilution buffer to make a total of 50 ml.
Dilute it with enzyme dilution buffer to adjust the concentration to within 2–4 U/ml.
Procedure
- Pipette accurately 5 ml of substrate suspension and 2 ml of distilled water into a test tube (24 mm i.d. × 200 mmH) and mix to start the preincubation at 37℃.
- After 10 min, add 0.5 ml of enzyme solution and mix to start the reaction.
※ In the case of a test blank, add 0.5 ml of enzyme dilution buffer in place of enzyme solution. - After 20 min, stop the reaction with 16 ml of reaction stopper.
- Add 3 drops of indicator and titrate the whole mixture with under nitrogen gas bubbling.
※ End point of titration: Appearance of the same color as that of the blank Titration volume sample : Vs blank : Vc △V = (Vs−Vc) ≦ 2.5 ml Vc ≦ 0.6 ml
Calculation
-
Activity (U/mg of powder) = {(△V×F)/20}× 50× 1/0.5 × 1/x
20 : reaction time (min) F : factor of titration solution (50 mM NaOH) 50 : concentration (mM) of titration solution
( 50 mM NaOH)0.5 : the volume of enzyme solution (ml) X : concentration of the sample in enzyme solution ( mg/ml)
Storage
-
Storage at−20℃ in the presence of a desiccant is
recommended. Enzyme activity will be retained for at least one year under this condition
References
- Yamaguchi, T., Muroya, N., Isobe, M. and Sugiura, M. (1973) Agric. Biol. Chem., 37, 999–1005.
- Sugiura, M., Isobe, M., Muroya, N. and Yamaguchi, T. (1974) Agric. Biol. Chem., 38, 947–952.
- Sugiura, M. and Isobe, M. (1974) Biochem. Biophys. Acta, 341, 195–200.
- Sugiura, M. and Isobe, M. (1975) Chem. Pharm. Bull., 23, 1226–1230.
- Horiuchi, Y., Koga, H. and Gocho, S. (1976) J. Biochem. (Tokyo) , 80, 367–370.
- Saiki, T., Takagi, Y. Suzuki, T., Narasaki, T., Tamura, G. and Arima, K. (1969) Agric. Biol. Chem., 33, 414.
LPM 活性測定法 (Japanese)
試薬液
- 基質懸濁液 (オリーブ油とアデカトールSO–120 の懸濁液)
「局方」オリーブ油50.0g とアデカトールSO–120
50.0g を精製水150ml に懸濁する。 - 反応停止液
エタノールーアセトン (1:1) 混液 - 指示液
1% (W/V) フェノールフタレンーエタノール溶液
- 滴定液
50mM NaOH 液 - 酵素溶解希釈用液
0.1% (W/V) BSA と0.1% (W/V) NaN3 を含む
0.1M KH2PO4–NaOH 緩衝液 pH8.0 - 試薬
オリーブ油:「局方」
エタノール:「局方」
アデカトールSO–120:ADEKA 製
BSA : Millipore 製 Fraction V pH5.2 #81–053
酵素試料液
- 検品約10mg を精密に量り、酵素溶解稀釈溶液に溶解して全容50ml とする。
その液を酵素溶解希釈用液で2~4U/ml 濃度となるように適宜希釈する。
測定操作法
- 試験管 (24mm i.d. × 200mm H) に基質懸濁液5mlと精製水2ml を正確に分注して攪拌混和後、37℃で予備加温する。
- 10 分経過後、酵素試料液0.50ml を加えて混和し、37℃で反応を開始する。
※ 盲検は酵素試料液の代わりに酵素溶解希釈用液0.50ml を加える。 - 20 分経過後、反応停止液16.0ml を加えて反応を停止する。
- 指示液3 滴を加えてN2 ガスで攪拌しながら滴定液で滴定する。
※ 滴定の終点は盲検時と同色 (淡赤色) を呈した時点とする。
求められた滴定量を試料液はVs、盲検液はVc とする。ΔV = (Vs−Vc) ≦ 2.5 ml Vc ≦ 0.6 ml
計算
活性 (U/mg) = {(ΔV×F)/20}×50 × 1/0.5 × 1/x| 20 : | 反応時間 (min) |
| F : | 滴定液 (50mM NaOH) のFactor |
| 50 : | 滴定液 (50mM NaOH) の濃度 (mM) |
| 0.5 : | 反応に供した酵素試料液量 (ml) |
| X : | 酵素試料液中の検品濃度 (mg/ml) |