OXALOACETATE DECARBOXYLASE [OACⅡ]
from Pseudomonas sp.
(Oxaloacetate carboxy–lyase, EC 4.1.1.3)
(Long–chain–fatty–acid–CoA ligase)
Oxaloacetate → Pyruvate + CO2
Preparation and Specification
- Appearance
- : White to off white amorphous powder, lyophilized
- Specific activity
- : More than 2300 U/mg solid
- Contaminants
- :
- AST (GOT)
- Less than 0.005 % (U/U)
- Catalase
- Less than 0.3 % (U/U)
Properties
- Molecular weight
- : 31 kDa (SDS–PAGE) , 120 kDa (Superdex 200)
- Isoelectric point
- : pH 5.16
- Michaelis constants
- : Oxaloacetate 3.3 × 10-3M
- Optimum pH
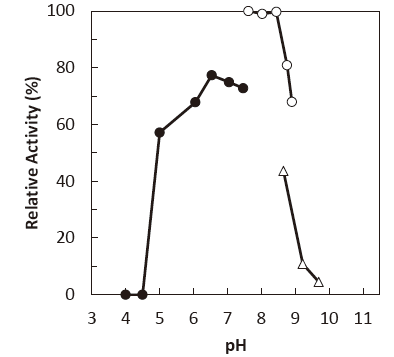
- : 7.5–8.5Figure 1
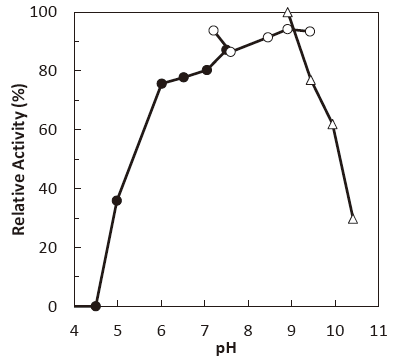
- pH stability
- : 7.5–9.0 (50℃, 3 hr.) Figure 2
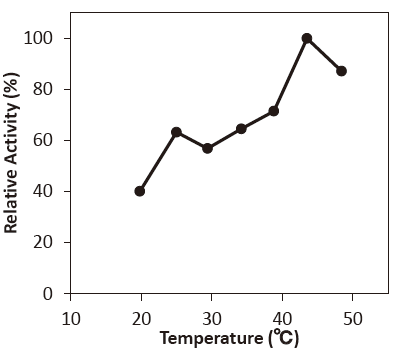
- Optimum temperature
- : 40–50℃Figure3
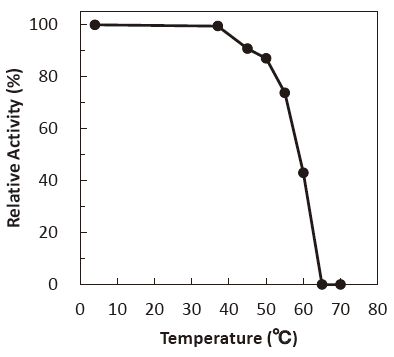
- Thermal stability
- : Stable at 50℃ and below (pH 7.0, 10 min) Figure4
- Storage stability
- : At least one year at -20℃
- Activators
- : Mg2+, Mn2+
- Inhibitors
- : Sodium dodecylsulfate, Sodium laurylbenzen sulfonate
Applications for Diagnostic Test
This enzyme is useful for enzymatic determination of AST when coupled with pyruvate oxidase (T–45)
| AST | ||
| Aspartic acid + α - ketoglutarate | → | Oxaloacetate + Glutamic acid |
| OACⅡ | ||
| Oxaloacetate | → | Pyruvate + CO2 |
| POPG | ||
| Pyruvate + O2 + H2O | → | Acetylphosphate + CO2 + H2O2 |
| POD | ||
| 2 H2O2 + 4-AA + Phenol | → | Quinoneimine dye + 4 H2O |
Assay
Principle
-
The assay is based on the decrease in absorbance at 340 nm as the consumption of NADH proceeds in the following reactions:
| OAC Ⅱ | ||
| Oxaloacetate | → | Pyruvate+CO2 |
| LDH | ||
| Pyruvate+NADH+H+ | → | Lactate+NAD+ |
LDH: Lactate dehydrogenase
NADH: Nicotineamide adenine dinucleotide
Unit definition
-
One unit is defined as the amount of enzyme which produces 1 μmole of pyruvate per minute at 25℃ under the conditions specified in the assay procedure.
Reagents
- Reaction mixture
0.1 M TEA–NaOH buffer pH 8.0 0.90 ml 10 mM MnCl2 solution 0.10 ml 6.5 mM NADH solution 0.10 ml Distilled water 0.90 ml - 550 U/ml LDH solution
Mix 0.1 ml of LDH solution (10 mg/2 ml, 2,750 U/ml) with 0.4 ml of 10 mM Tris–HCl buffer pH 7.0
- Substrate solution (50 mM oxaloacetate solution)
Dissolve 33 mg of oxaloacetate with 5 ml of 0.2 M Tris–HCl buffer pH 9.0.
- Enzyme dilution buffer
10 mM Tris–HCl buffer pH 8.0
- Reagents
TEA (Triethanolamine, HCl salt) : Merck Co.
MnCl2 ・ 4H2O:
FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corporation
Special grade #133–00725
-
NADH (2Na・3H2O, Reduced form) :
Kyowa Hakko Co., Ltd.LDH: Roche Diagnostics GmbH #10 127 876 001
Oxaloacetate:
FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corporation #150-00411
Enzyme solution
-
Accurately weigh about 20 mg of the sample and add enzyme dilution buffer to make a total of 20 ml. Dilute it with enzyme dilution buffer to adjust the concentration to within 0.5–1.4 U/ml.
Procedure
- Pipette accurately 2.0 ml of reaction mixture, 20 μl of LDH solution and 50 μl of enzyme solution into a samll test tube and preincubate at 25℃.
※ In the case of a test blank, add 50 μl of enzyme dilution buffer in place of enzyme solution. - After 5 min, add 100 μl of substrate solution and mix to start the reaction at 25℃.
- After starting the reaction, measure the rate of decrease per minute in absorbance at 340 nm. The rate must be measured within the linear portion of the absorbance curve.
-
△A/min = (As/min-Ab/min) ≦ 0.15 Abs/minAbsorbance sample : As/min blank : Ab/min
Calculation
-
Activity (U/mg of powder) = {(△ A/min)/(6.22)} × 2.17/0.05 × 1/x
6.22 : millimolar extinction coefficient of NADH at 340 nm (cm2/ μmole) 2.17 : final volume (ml) 0.05 : volume of enzyme solution (ml) X : concentration of the sample in enzyme solution ( mg/ml)
Storage
-
Storage at -20℃ in the presence of a desiccant is recommended. Enzyme activity will be retained for at least one year under this condition.
References
- Horton, A. A. and Kornberg, H. L. (1964) Biochem.
Biophys. Acta, 89, 381–383. - Schmitt, A., Bottke, I. and Siebert, G. (1966) Hoppe–Seyler’s Z. Physiol. Chem., 347, 18–34.
OAC Ⅱ活性測定法 (Japanese)
試薬液
- 反応試薬混合液
0.1M TEA–NaOH 緩衝液 pH8.0 0.90 ml 10mM 塩化マンガン溶液 0.10 ml 6.5mM NADH 溶液 0.10 ml 精製水 0.90 ml - 550U/ml LDH 溶液
ロシュ製LDH 溶液 (10mg/2ml 2,750U/ml) の0.1ml と10mM トリス–HCl 緩衝液pH7.0 を0.4ml混合する。 - 基質溶液 (50mM オキサロ酢酸溶液)
オキサロ酢酸33mg を0.2M トリス–HCl 緩衝液pH9.0 5ml で溶解する。 - 酵素溶解希釈用液
10mM トリス–HCl 緩衝液pH8.0 - 試薬
TEA (トリエタノールアミン・塩酸塩) :メルク製
塩化マンガン (MnCl2 ・ 4H2O) :富士フイルム和光純薬製 特級 #133–00725NADH (ニコチンアミドアデニンジヌクレオチド・2Na・3H2O・還元型) : 協和発酵製
LDH (乳酸脱水素酵素) :ロシュ製 #10 127 876 001
オキサロ酢酸:富士フイルム和光純薬製 #150-00411
酵素試料液
- 検品約20mg を精密に量り、酵素溶解希釈用液で溶解して全容20ml とする。その液を酵素溶解希釈用液で0.5~1.4U/ml 濃度となるように適宜希釈する。
測定操作法
- 小試験管に反応試薬混合液2.0ml とLDH 溶液20 μl及び酵素試料液50 μl を正確に分注して25℃で予備加温する。
※ 盲検は酵素試料液の代わりに酵素溶解希釈用液50μl を加える。
- 5 分経過後、基質溶液100 μl を加えて混和し、25℃で反応を開始する。
- 反応開始後、340nm における吸光度を測定して直線的に反応している1 分間当たりの吸光度変化を求める。
求められた吸光度変化を試料液はAs/min、盲検液はAb/min とする。
ΔA/min = (As/min−Ab/min) ≦ 0.15 Abs/min
計算
活性 (U/mg) = {(ΔA/min)/(6.22)} × 2.17/0.05 × 1/x| 6.22 : | NADH の340nm におけるミリモル分子吸光係数 (cm2 /μmole) |
| 2.17 : | 反応総液量 (ml) |
| 0.05 : | 反応に供した酵素試料液量 (ml) |
| X : | 酵素試料液中の検品濃度 (mg/ml) |