ALCOHOL OXIDASE [ALOD]
from Candida sp.
(Alcohol: oxygen oxidoreductase, EC 1.1.3.13)
R–CH2OH + O2 → R–CHO + H2O2
Preparation and Specification
- Appearance
- : Light yellowish amorphous powder, lyophilized
- Specific activity
- : More than 7 U/mg solid
Properties
- Substrate specificity
- : See Table 1
- Molecular weight
- : 520 kDa (gel filtration)
75 kDa (SDS–PAGE)
- Isoelectric point
- : pH 4.1
- Michaelis constants
- : Methanol 2.9 × 10-3M
Ethanol 8.2 × 10-3M
- Optimum pH
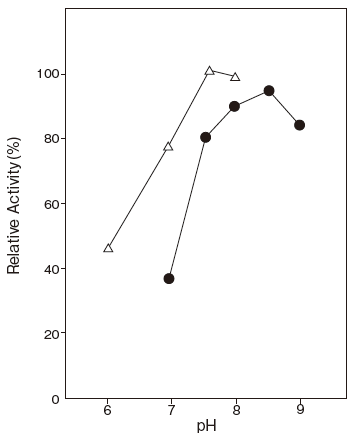
- : 7.5–9.0Figure 1
- pH stability
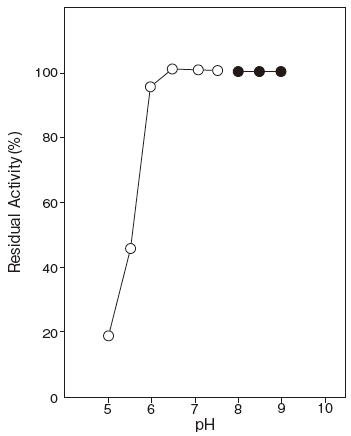
- : 6.0–9.5 (37℃, 60 min) Figure 2
- Thermal stability
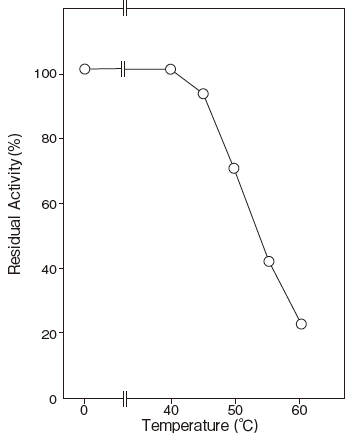
- : Stable at 40℃ and below (pH 7.5, 10 min) Figure 3
- Effect of chemicals
- : See Table 2 and Table 3
Applications for Diagnostic Test
This enzyme is useful for enzymatic determination of blood alcohol.
| ALOD | ||
| R-CH2OH + O2 | → | R-CHO + H2O2 |
| POD | ||
| 2 H2O2 + 4-AA + Phenol | → | Quinoneimine dye + 4 H2O |
Table 1.Substrate specificity
| Substrate | Relative activity (%) |
|---|---|
| Methanol | 100 |
| Ethanol | 79.3 |
| n–Propanol | 46.5 |
| iso–Propanol | 25.8 |
| n–Butanol | 39.6 |
| Form aldehyde | 48.2 |
| Acetoaldehyde | 0 |
Table 2. Effect of metal ions on ALOD activity
| Metal ion | Concentration (mM) |
Relative activity (%) |
|---|---|---|
| None | – | 100.0 |
| KCl | 10 | 103.4 |
| NaCl | 10 | 99.3 |
| LiCl | 10 | 99.3 |
| NH4Cl | 10 | 95.2 |
| MgCl2 | 1 | 100.0 |
| CaCl2 | 1 | 93.1 |
| CoCl2 | 1 | 68.4 |
| BaCl2 | 1 | 69.8 |
| NiCl2 | 1 | 70.5 |
| MnCl2 | 1 | 100.6 |
| EDTA | 1 | 108.2 |
Table 3. Effect of detergents on ALOD activity
| Detergent | Concentration (%) |
Relative activity (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Nonidet P–40 | 0.1 | 96.3 |
| Triton X–100 | 0.1 | 98.7 |
| Adekatol PC–8 | 0.1 | 91.5 |
| Adekatol SO–120 | 0.1 | 96.3 |
| Tween 80 | 0.1 | 98.7 |
| Briji 35 | 0.1 | 95.1 |
| Deoxycholate | 0.1 | 69.8 |
Assay
Principle
-
The assay is based on the increase in absorbance at 480 nm as the formation of quinoneimine dye proceeds in the following reactions:
| ALOD | ||
| CH3OH+O2 | → | HCHO+H2O2 |
| POD | ||
| 2 H2O2+4–AA+Phenol | → | Quinoneimine dye+4 H2O |
Unit definition
-
One unit is defined as the amount of enzyme which generates 1 μmole of H2O2 and formaldehyde from methanol per minute at 37℃ under the conditions specified in the assay procedure.
Reagents
- Reaction mixture
0.2 M Tris–HCl buffer pH8.0 0.20ml 15 mM 4–AA solution 0.10ml 0.2% (W/V) Phenol solution 0.10ml 2.0 M Methanol solution 0.25ml
-
50 U/ml POD solution 1) 0.10 ml Distilled water 0.25 ml 1) : 50 U/ml POD solution
Dissolve 500 U (PPU) of POD with 10 ml of distilled water. - Reaction stopper
Ethanol - Enzyme dilution buffer
10 mM Tris–HCl buffer pH 8.0 - Reagents
4–AA: NACALAI TESQUE, INC. Special grade #01907–52
POD: Sigma Chemical Co. Type Ⅱ #P–8250
Ethanol: FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical CorporationJapanese Pharmacopoeia Grade #324–00015
Enzyme solution
-
Accurately weigh about 20 mg of the sample and add enzyme dilution buffer to make a total of 20 ml. Dilute it with enzyme dilution buffer to adjust the concentration as required.
Procedure
- Pipette accurately 1.0 ml of reaction mixture into a small test tube and preincubate at 37℃.
- After 5 min, add exactly 50 μl of enzyme solution and mix to start the reaction at 37℃.
※ In the case of a test blank, add 50 μl of enzyme dilution buffer in place of enzyme solution. - At 5 min after starting the reaction, add 2.0 ml of the reaction stopper to stop the reaction.
- Measure the absorbance at 480 nm.
Absorbance sample : As
-
△A = (As-Ab) ≦ 0.20 Absblank : Ab/min
Calculation
Activity (U/mg of powder) = {(△ A/5)/(17.17 × 1/2)} × 3.05/0.05 × 1/x| 17.17 : | millimolar extinction coefficient of quinoneimine dye at 480 nm (cm2 / μmole) |
| 1/2 : | a multiplier derived from the fact that 2 mole of H2O2 produces 1 mole of quinoneimine dye |
| 5 : | reaction time (min) |
| 3.05 : | final volume (ml) |
| 0.05 : | volume of enzyme solution (ml) |
| X : | concentration of the sample in enzyme solution (mg/ml) |
Storage
Storage at -20℃ in the presence of a desiccant is recommended.
References
- Fujii, T. and Tonomura. K. (1972) Agric. Biol. Chem., 36, 2297–2306.
- Sahm, H. and Wagner, F. (1973) Eur. J. Biochem., 36, 250–256.
- Kato, N., Omori, Y., Tani. Y. and Ogata. K. (1976) Eur. J. Biochem., 64, 341–350.
- Tani, Y., Miya, T., Nishikawa. H. and Ogata. K (. 1972) Agric. Biol. Chem., 36, 68–75.
ALOD 活性測定法 (Japanese)
試薬液
- 反応試薬混合液
0.2Mトリス–HCl 緩衝液 pH8.0 0.20 ml 15mM 4–AA 溶液 0.10 ml 0.2% (W/V) フェノール溶液 0.10 ml 2M メタノール液 0.25 ml 50U/ml POD 溶液 1) 0.10 ml 精製水 l 0.25 m 1) : 50U/ml POD 溶液
POD 500 単位 (PPU) を精製水10ml で溶解する。 - 反応停止液
エタノール原液をそのまま使用する。 - 酵素溶解希釈用液
10mM トリス–HCl 緩衝液 pH8.0 - 試薬
4–AA:ナカライテスク製 特級 #01907–52
POD:シグマ製 Type Ⅱ #P–8250
エタノール:富士フイルム和光純薬製日本薬局方 #324–00015
酵素試料液
- 検品約20mg を精密に量り、酵素溶解希釈用液に溶解して全容20ml とする。
その液を酵素溶解希釈用液で適宜希釈する。
測定操作法
- 小試験管に反応試薬混合液1.0ml を正確に分注して37℃で予備加温する。
- 5 分経過後、酵素試料液50 μl を正確に加えて混和後、37℃で反応を開始する。
※ 盲検は酵素試料液の代わりに酵素溶解希釈用液50μl を加える。 - 5 分経過後、反応停止液2.0ml を正確に加え反応を停止する。
- 480nm における吸光度を測定する。
求められた吸光度を試料液はAs、盲検液はAb とする。
ΔA = (As-Ab) ≦ 0.20 Abs
計算
-
活性 (U/mg) = {(△ A/5)/(17.17 × 1/2)} × 3.05/0.05 × 1/x
17.17 : キノンイミン色素の480nm におけるミリモル分子吸光係数 (cm2/ μmole) 1/2 : H2O2 2 モルからキノンイミン色素1 モルが生成することによる係数 5 : 反応時間 (min) 3.05 : 反応総液量 (ml) 0.05 : 反応に供した酵素試料液量 (ml) X : 酵素試料液中の検品濃度 (mg/ml)