L–α–GLYCEROPHOSPHATE OXIDASE [GPOSP]
from Streptococcus sp.
(sn –Glycero–3–phosphate: oxygen 2–oxidoreductase, EC 1.1.3.21)
L–α–Glycerophosphate + O2 → Dihydroxyacetone phosphate + H2O2
| ★ | Advantages | |
| ① | Highly purified enzyme | |
| ② | Stability in solution | |
| ③ | Registance for antiseptic reagents | |
Preparation and Specification
- Appearance
- : Yellowish amorphous, lyophilized
- Specific activity
- : More than 40 U/mg solid
- Contaminants
- :
- Acetate kinase
- Less than 0.1 % (U/U)
- Lactate oxidase
- Less than 0.001% (U/U)
Properties
- Substrate specificity
- : See Table 1
- Molecular weight
- : 180 kDa (Sephacryl S–200)
130 kDa (Sephadex G200)
67 kDa (SDS–PAGE)
- Isoelectric point
- : pH 4.03
- Michaelis constants
- : L–α–Glycerophosphate 2.23 mM (pH 6.5)
4.18 mM (pH 7.5)
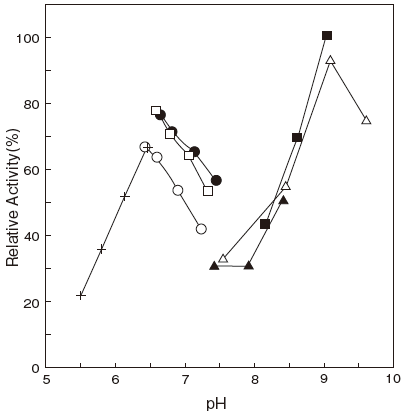
- Optimum pH
- : 6.5 and 8.5–9.0Figure 1
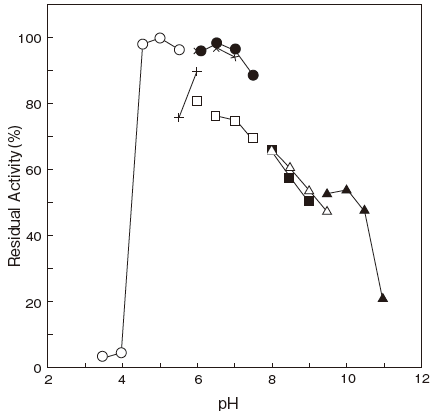
- pH stability
- : 5.0–7.0 (37℃, 30 min) Figure 2
- Optimum temperature
- : 37℃
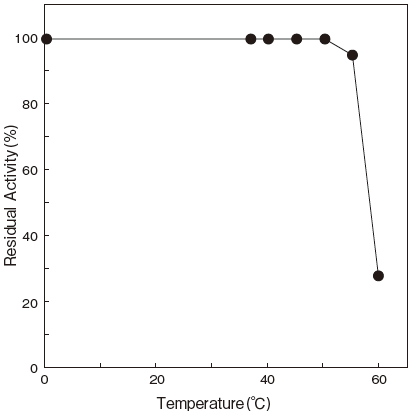
- Thermal stability
- : Stable at 55℃ and below
(100 mM Phosphate buffer pH 6.5, 5 min.) Figure3
- Effect of various chemicals
- : See Table 2
- Stabilizers
- : FAD, Sucrose
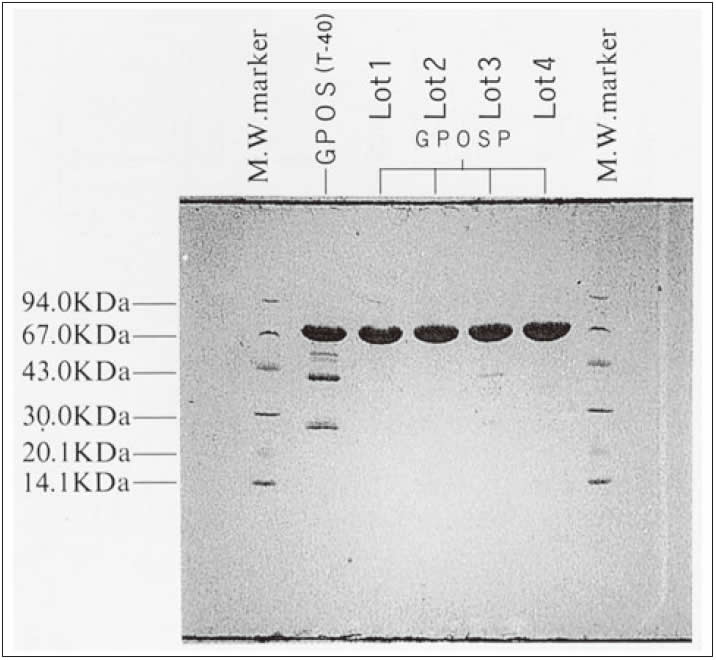
- Electrophoresis pattern
- : See Figure 4
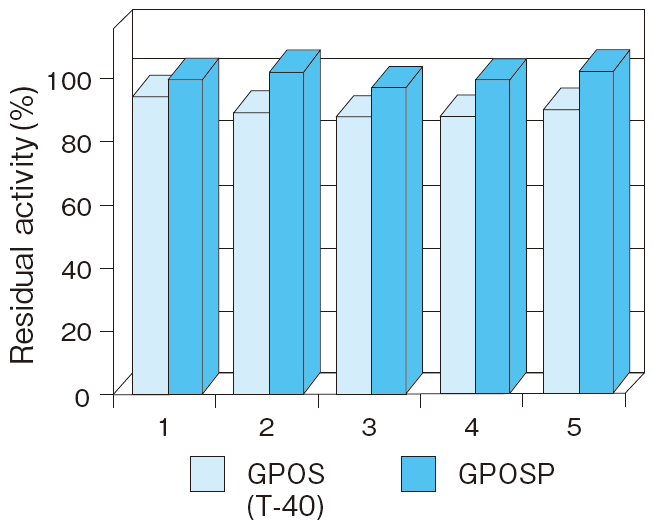
- Liquid stability (Buffer pH)
- : See Figure 5
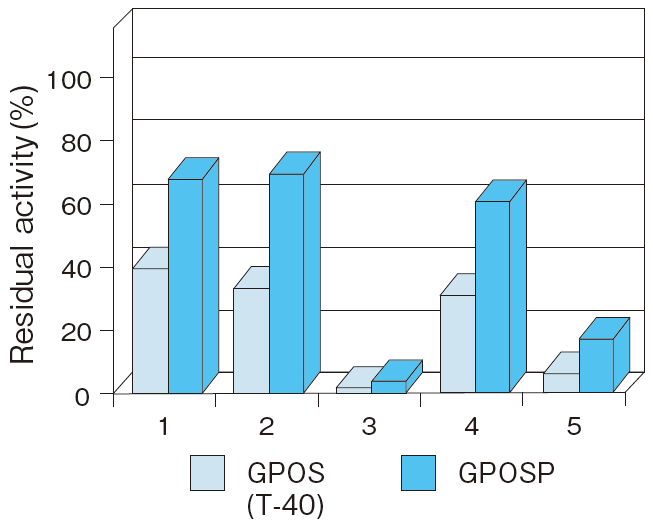
- (Detergents)
- : See Figure 6
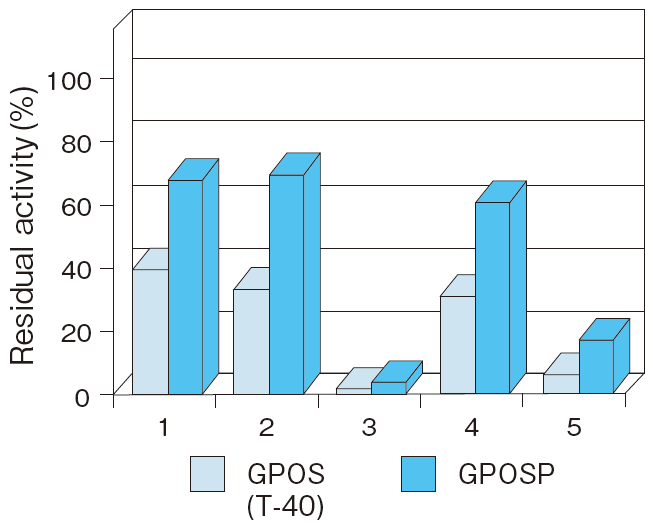
- Antiseptic stability
- : See Figure 7
- Turbidity test
- : See Table 3
Applications for Diagnostic Test
This enzyme is useful for enzymatic determination of triglyceride.
| LP | ||
| TG + 3 H2O | → | Glycerol + 3 Fatty acid |
| GKZ | ||
| Glycerol + ATP | → | G-3-P + ADP |
| GPOSP | ||
| G-3-P + O2 | → | DHAP + H2O2 |
| POD | ||
| 2 H2O2 + 4-AA + Phenol | → | Quinoneimine dye + 4 H2O |
TG: Triglyceride, DHAP: Dihydroxyacetone phosphate
Table 1. Substrate specificity
| Substrate (300mM) | Relative activity (%) |
|---|---|
| L–α–Glycerophosphate |
100 |
| Glucose–1–phosphate |
0 |
| Glucose–6–phosphate |
0 |
| Glycerol |
0 |
| Glucose | 0 |
Table 3. GPOSP Turbidity test
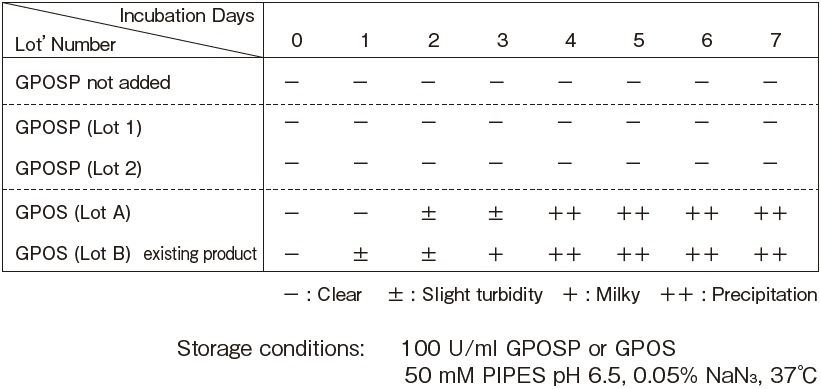
Table 2. Effect of various chemicals on COD activity
| Additives | Consentration | Relative activity (%) |
|---|---|---|
| None |
2mM | 100 |
| MgCl2 |
2mM | 101 |
| MgSO4 |
2mM | 102 |
| ZnCl2 |
2mM | 102 |
| ZnSO4 |
2mM | 102 |
| NaCl |
2mM | 103 |
| NH4Cl |
2mM | 103 |
| BaCl2 | 2mM | 103 |
| Ba (CH3COO) 2 |
2mM | 101 |
| NiCl2 | 2mM | 103 |
| CoCl2 | 2mM | 103 |
| MnCl2 | 2mM | 114 |
| LiCl |
2mM | 103 |
| KCl |
2mM | 102 |
| CaCl2 | 2mM | 103 |
| EMULGEN 810 |
0.1% | 98 |
| EMULGEN 911 |
0.1% | 98 |
| RHEODOL TWL–106 |
0.1% | 99 |
| RHEODOL 460 |
0.1% | 99 |
| ADEKANOL NP–720 |
0.1% | 99 |
| Triton X–100 |
0.1% | 99 |
| Triton X–305 |
0.1% | 98 |
| Tween 80 | 0.1% | 100 |
Fig.5 Liquid stability of GPOSP (Buffer, pH)
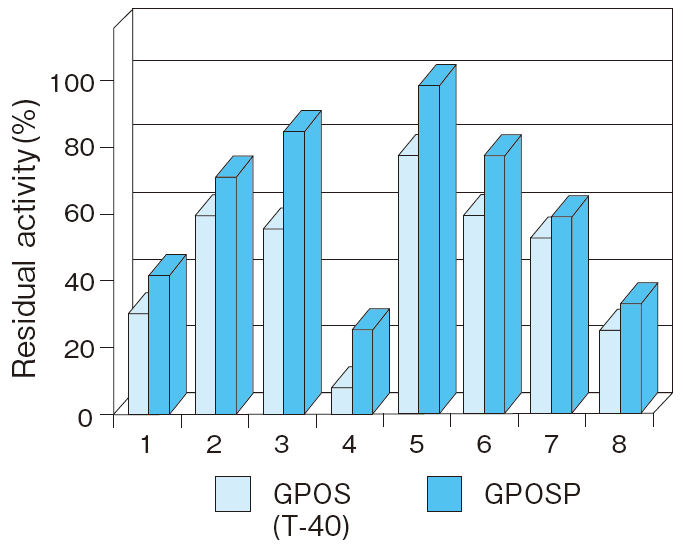
1:MES pH 6.5
2:Bis-Tris pH 6.0
3:Bis-Tris pH 6.5
4:Bis-Tris pH 7.0
5:PIPES pH 6.0
6:PIPES pH 6.5
7:PIPES pH 7.0
8:MOSPO pH 7.0
Incubation conditions : 37℃ for 7 days
Fig.6 Liquid stability of GPOSP (Influence of detergents)
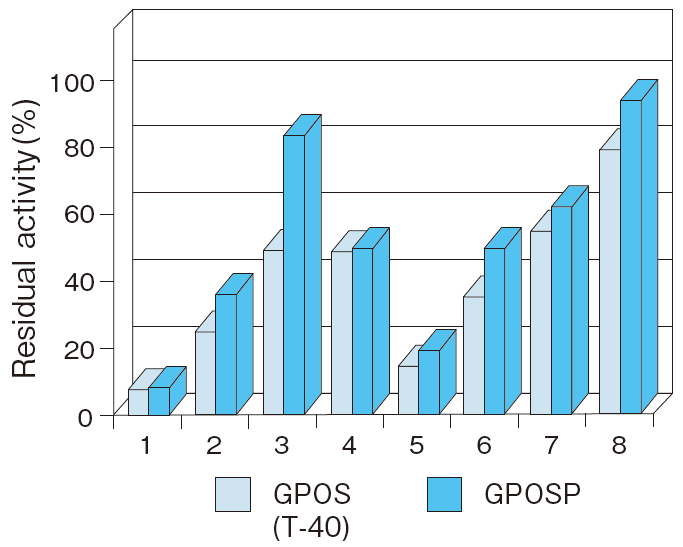
1:EMULGEN 709
2:EMULGEN B-66
3:RHEODOL TWL-106
4:RHEODOL 460
5:Adekatol SO-120
6:Adekatol B-795
7:Triton X-100
8:Triton X-305
Incubation conditions : 37℃ for 7 days
Assay
Principle
-
The assay is based on the increase in absorbance at 600 nm as the formation of quinoneimine dye in the following reactions:
| GPOSP | ||
| L–α–Glycerophosphate + O2 | → | Dihydroxyacetone phosphate+H2O2 |
| POD | ||
| 2H2O2+4–AA+DAOS | → | Quinoneimine dye+4H2O |
DAOS : [3, 5–dimethoxy–N–ethyl–N– (2–hydroxy–3– sulphopropyl) aniline]
Unit definition
-
One unit is defined as the amount of enzyme which generates 1 μmole of H2O2 per minute at 37℃ under the conditions specified in the assay procedure.
Reagents
- Reaction mixture
Dissolve 6.05g of PIPES and 9.45 g (purity calculation) of Disodium Glycerophosphate with 70 ml of distilled water and adjust pH to 6.5 with 4 N NaOH at 25℃.
Add all reagents listed below and confirm pH is 6.5 at 25℃. Add distilled water to make a total of 100 ml.100 U/ml POD 1) solution 5.0 ml 15 mM 4–AA solution 10.0 ml 100 mM DAOS solution 1.0 ml 5% (W/V) Triton X–100 solution 1.0 ml 1) : 100 U/ml POD solution
Dissolve 1,000 U (PPU) of POD with 10 ml of distilled water. - Reaction stopper
0.5% (W/V) SDS solution
SDS: Sodium dodecyl sulfate - Enzyme dilution buffer
10 mM PIPES-NaOH buffer pH 6.5 - Reagents
PIPES[Piperazine–1,4–bis (2–ethanesulfonic acid) ]:Dojindo Laboratories #345–02225DAOS (sodium salt) : Dojindo Laboratories #OC06
4–AA: NACALAI TESQUE, INC.Special grade #01907–52Triton X–100: The Dow Chemical Company
Disodium Glycerophosphate 5.5 Hydrate :FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical CorporationSDS (Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate) :
#192–02055NACALAI TESQUE, INC. Extra pure #31606–75POD: Sigma Chemical Co. Type Ⅱ #P–8250
Enzyme solution
-
Accurately weigh about 20 mg of the sample and add enzyme dilution buffer to make a total of 20 ml. Dilute it with enzyme dilution buffer to adjust the concentration as required.
Procedure
- Pipette accurately 1.0 ml of reaction mixture into a small test tube and preincubate at 37℃.
- After 5 min, add exactly 20 μl of enzyme solution and mix to start the reaction at 37℃.
※ In the case of a test blank, add 20 μl of enzyme dilution buffer in place of enzyme solution. - At 5 min after starting the reaction, add 2.0 ml of the reaction stopper to stop the reaction.
- Measure the absorbance at 600 nm.
0.050 Abs ≦ △A (As−Ab) ≦ 0.250 AbsAbsorbance sample : As blank : Ab
Calculation
-
Activity (U/mg of powder) = {(△A/5)/(16.8×1/2)}×3.02/0.02×1/x
16.8 : millimolar extinction coefficient of quinoneimine dye at 600 nm (cm2/μmole) 1/2 : a multiplier derived from the fact that 2 mole of H2O2 produces 1 mole of quinoneimine dye 5 : reaction time (min) 3.02 : final volume (ml) 0.02 : volume of enzyme solution (ml) X : concentration of the sample in enzyme solution ( mg/ml)
Storage
-
Storage at −20℃ in the presence of a desiccant is recommended. Enzyme activity will be retained for at least one year under this condition.
References
- Jacobs, N. J. and Van Demark, P. J. (1960) Arch.
Biochem. Biophys., 88, 250–255. - Koditschek, L. K. and Umbreit, W. W. (1969) J. Bacteriol., 98, 1063–1068.
- Gancedo, C., Gancedo, J. M. and Sols, A. (1968) J. Biochem., 5, 165–172.
- Kistler, W. S., Hirsch, C. A., Cozzarelli, N. R. and Lin, E. C. C. (1969) J. Bacteriol., 100, 1133–1135.
- Esders, T. W. and Michrina, C. A. (1979) J. Biol. Chem., 254, 2710–2715.
GPOSP活性測定法 (Japanese)
試薬液
- 反応試薬混合液
PIPES 6.05g とグリセロりん酸2Na 9.45g (純度換算) を精製水70ml に溶解した後、4N NaOH でpH6.5 (25℃) に調整し、その液に下記試薬を加えて混和し、pH6.5 (25℃) であることを確認した後、精製水で全容100ml とする。100U/ml POD 溶液1)
5.0 ml 15mM 4–AA 溶液 10.0 ml 100mM DAOS 溶液 1.0 ml 5% (W/V) トリトンX–100 溶液 1.0 ml 1) : 100U/ml POD 溶液
POD 1,000 単位 (PPU) を精製水10ml で溶解する。 - 反応停止液
0.5% (W/V) SDS 溶液 - 酵素溶解希釈用液
10mM PIPES–NaOH 緩衝液 pH6.5 - 試薬
PIPES[ピペラジン–1,4– ビス (2– エタンスルホン酸) ]:同仁化学製 #345–02225
DAOS[3,5– ジメトキシ–N– エチル–N– (2– ヒドロキシ–3– スルフォプロピル) アニリン]:同仁化学製 #OC064–AA:ナカライテスク製 特級 #01907–52
トリトンX–100:Dow Chemical 製
グリセロりん酸二ナトリウム5.5 水和物:富士フイルム和光純薬製 #192–02055SDS (ドデシル硫酸ナトリウム) :ナカライテスク製 一級 #31606–75POD:シグマ製 Type Ⅱ #P–8250
酵素試料液
- 検品約20mg を精密に量り、酵素溶解希釈用液で溶解して全容20ml とする。
その液を酵素溶解希釈用液で適宜希釈する。
測定操作法
- 小試験管に反応試薬混合液1.0ml を正確に分注し、37℃で予備加温する。
- 5 分経過後、酵素試料液20 μl を正確に加えて混和し、37℃で反応を開始する。
※ 盲検は酵素試料液の代わりに酵素溶解希釈用液20μl を加える。 - 5 分経過後、反応停止液2.0ml を加えて混和し、反応を停止する。
- 600nm における吸光度を測定する。
求められた吸光度を試料液はAs、盲検液はAb とする。
0.050 Abs ≦ ΔA = (As-Ab) ≦ 0.250 Abs
計算
活性 (U/mg) = {(△A/5)/(16.8×1/2)}×3.02/0.02×1/x| 16.8 : | キノンイミン色素の600nm におけるミリモル分子吸光係数 (cm2 /μmole) |
| 1/2 : | H2O2 2 モルからキノン色素1 モルが生成することによる係数 |
| 5 : | 反応時間 (min) |
| 3.02 : | 反応総液量 (ml) |
| 0.02 : | 反応に供した酵素試料液量 (ml) |
| X : | 酵素試料液中の検品濃度 (mg/ml) |