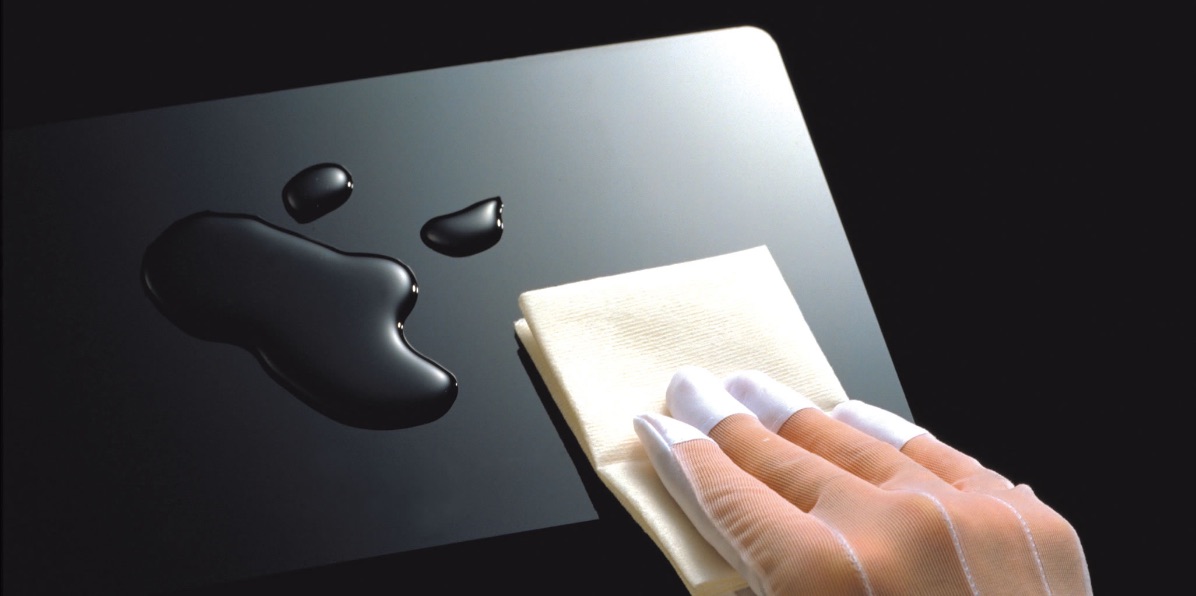
Low particle generation
check the video
- Low fallen fibersWe divide particles into the following categories
-
Particles
- Fallen fibersFallen particles 100μm or larger and visible to the human eye
- Micro particlesThat are not visible, but can be measured by a particle counter(0.1μm or larger)
Fallen fibers comparison
Wipes are immersed in 300 ml of deionized water and subjected to ultrasonic treatment for 15 minutes.
Remaining fibers filtered by filter paper is counted
Test Method : Asahi Kasei Method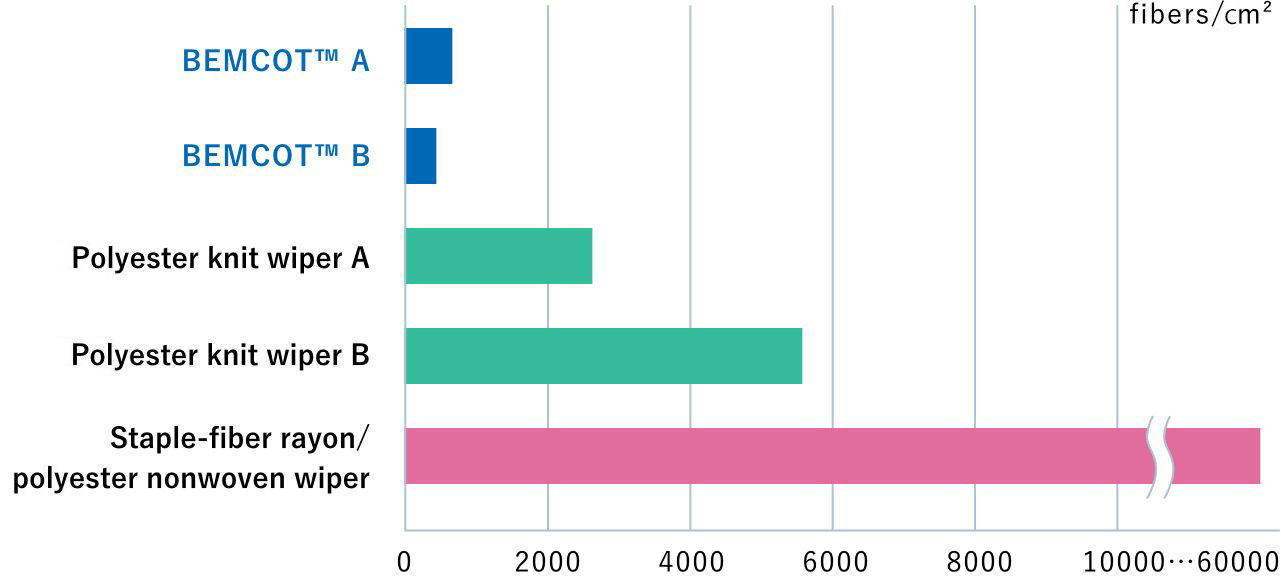
Comparison of fallen fibers performance by each testing method
General cellulose nonwoven wipes are made of short fibers.
Therefore their fibers can easily fall due to the friction from wiping and when immersed in liquid. Since BEMCOT™ is made of a continuous filament, fallen fibers can be reduced.Test1Wet agitation test
Wipes are immersed in 300 ml of deionized water and subject to ultrasonic treatment for 15 minutes. The water is then filtered. The photo shows the fallen fibers filtered by the filter paper.
Test Method : Asahi Kasei Method
BEMCOT™ 
Polyester
knit wiper
Staple-fiber rayon/
polyester nonwoven wiper
Papar wiper
(wood-pulp)Test2Fluffing after wiping test
A silicone board is wiped with a fixed load and at a fixed speed. Fluffing on the surface of wipes is compared after wiping.(Load: 22.2 g/m2; Speed: 1.0 m/min1; Distance: 40 cm)
Test Method : Asahi Kasei Method- BEMCOT™
-
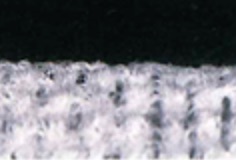
Wiping with a fixed load and at a fixed speed
Almost no fluffing and single yarn damage is observed the surface

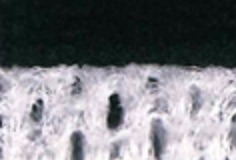
- Polyester knit wiper
-

Wiping with a fixed load and at a fixed speed

The knitting structure is broken by friction.Fluffing and single yarn damage is observed.

- Staple-fiber rayon/
polyester nonwoven wiper -

Wiping with a fixed load and at a fixed speed

Major fluffing is caused by friction.Single yarns are cut and damaged.

Test3Adhesive cellophane tape
peel-off testPlace a piece of adhesive cellophane tape on the wiper surface and compare the amount of fibers adhered to the tape after peeling it off.
Test Method : Asahi Kasei Method
BEMCOT™ 
Polyester
knit wiper
Staple-fiber rayon/
polyester nonwoven wiper
Papar wiper
(wood-pulp)
- Low microparticles
-
Microparticles
- Airborne microparticlesParticles generated in the air(0.3μm or larger)
- Liquid microparticlesParticles generated in liquid(0.1μm or larger)
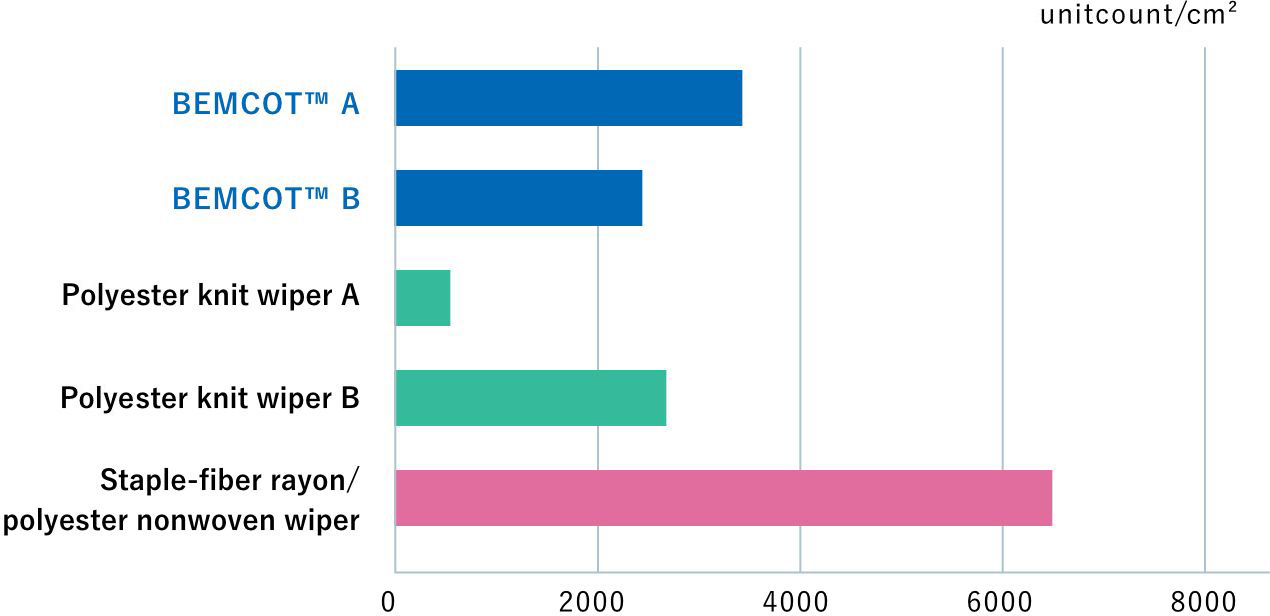
Microparticle comparison
Test Method : IES-RP-CCOO4.2 section 5.2 (Bixal shake test)
Liquid microparticle
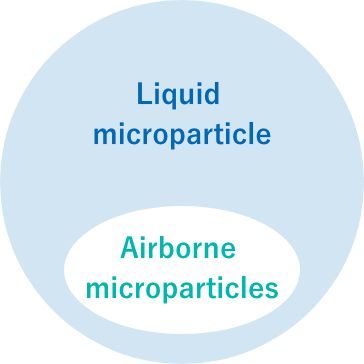
Category of Dry and Wet microparticles
Airborne microparticles only take up a small part of liquid microparticles.

Composites of liquid
microparticleMore than half of the wet microparticles are inorganic substances such as aluminum and silicon, though organic substances are also present.
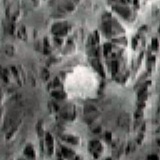
Composites of airborne microparticles
Organic substances in the wiper’s body; e.g., cellulose,polyester.
Problems of airborne microparticles test
Airborne microparticles can be measured comparatively easily by using a tumbler (photo) or particle counter, which are commercially available. These methods, however, pose many problems.
Static-charge buildup by synthetic-fiber wipes
Electrostatic retention of
microparticles in wipesImpact absorption
by soft wipesLow physical stress in wipes,reducing
microparticle generation and resulting in low countOnly a part of the airborne microparticles
among all those actually generated is measured.
Tumbler
This rotates a wiper in the SUS tube and measures the particles generated in the air.
Importance of liquid microparticles
It is more important to evaluate particles with wet condition since wipes are normally used in wet conditions such as with solvent absorbed or for wiping liquid.
