CHOLESTEROL ESTERASE [CENII]
from Pseudomonas sp.
(Sterol esterase)
Cholesterol ester + H2O → Cholesterol + Fatty acid
Preparation and Specification
- Appearance
- : White to pale brownish amorphous powder, lyophilized
- Specific activity
- : More than 100 U/mg solid
Properties
- Substrate specificity
- : See Table 1
- Molecular weight
- : 30kDa (SDS–PAGE)
- Isoelectric point
- : pH 5.28
(estimated from amino acid sequence)
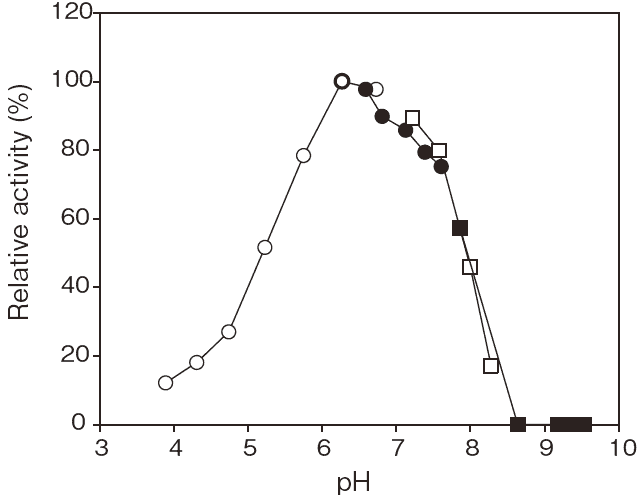
- Optimum pH
- : 6.5Figure 1
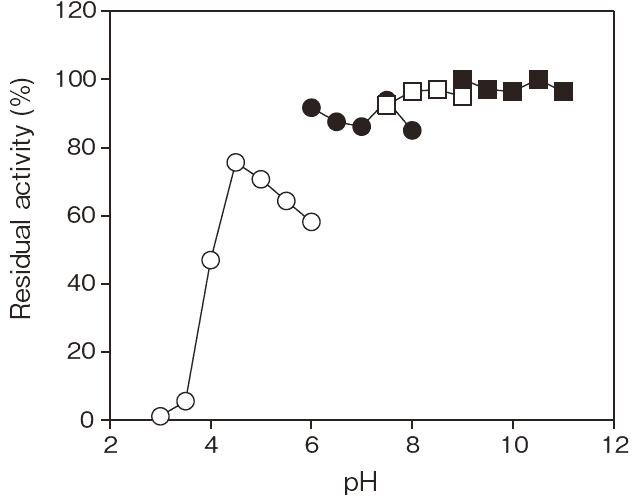
- pH stability
- : 6.0–11.0
(37°C, 60 min, in 0.1% BSA)Figure 2
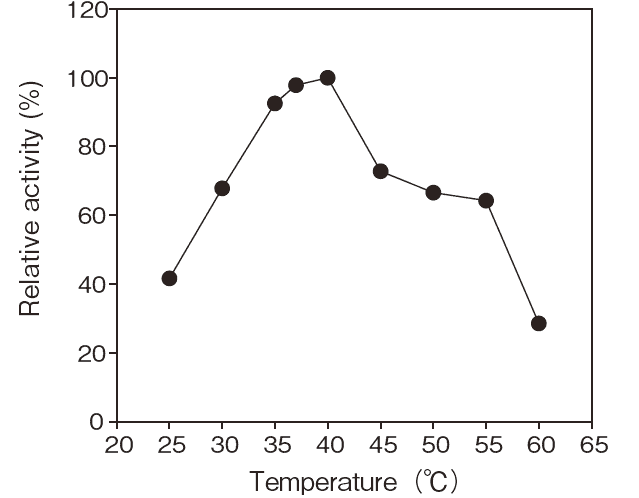
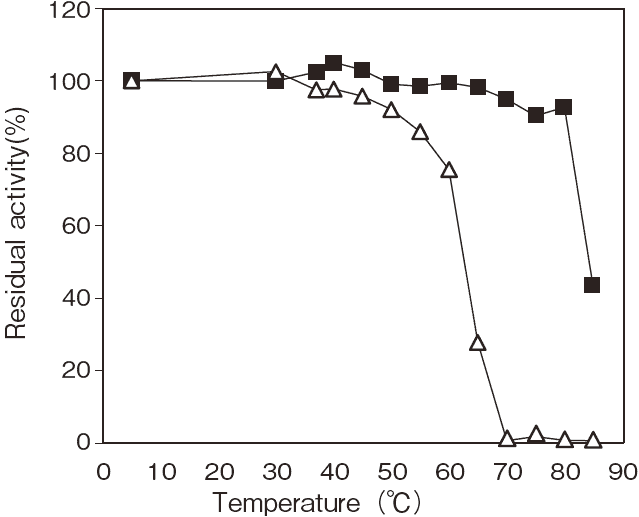
- Optimum temperature
- : 35-40°C
(Phosphate Buffer)Figure 3
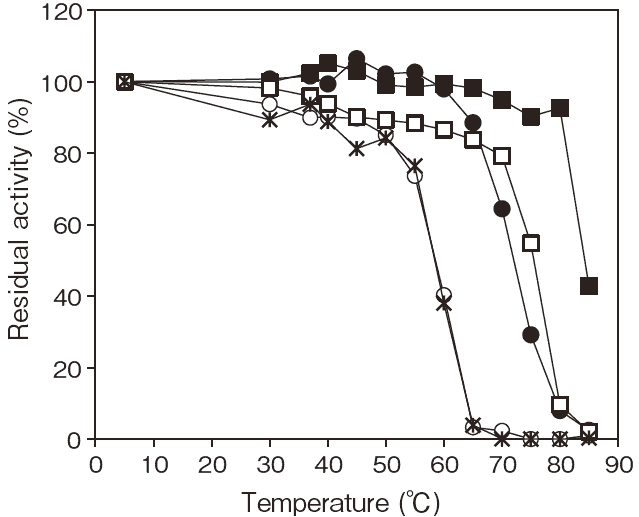
- Thermal stability
- : Stable at 45°C and below
(pH 8.0, 30min)Figure 4
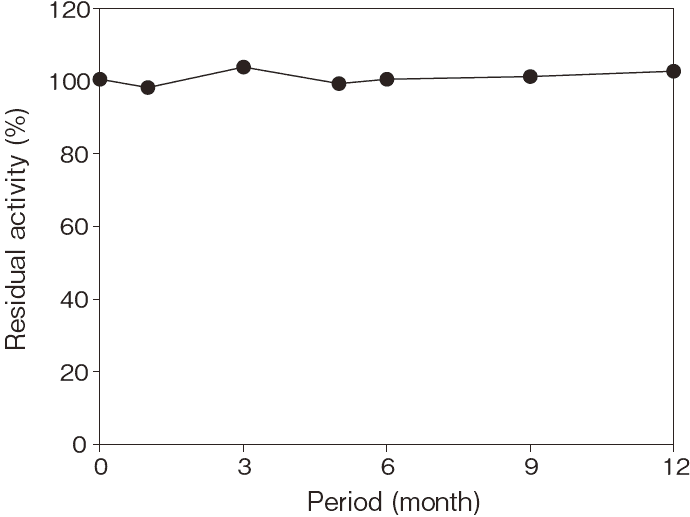
- Storage stability
- : At least one year at –20°CFigure 6
- Effect of coexisting ions
- : See Table 2
- Effect of detergents
- : See Table 3
- Activator
- : Adekatol TN-100, Adekatol PC-8, Adelatol SO-120,
Adekatol SO-135, Triton X-100
Applications for Diagnostic Test
This enzyme is useful for enzymatic determination of total cholesterol, HDL-C, and LDL-C coupled with cholesterol oxidase (T–101).
| CENII | ||
| Cholesterol ester + H2O | → | Cholesterol + FFA |
| CONII-FD | ||
| Cholesterol + O2 | → | Cholestenone + H2O2 |
| POD | ||
| 2 H2O2 + 4-AA + Phenol | → | Quinoneimine dye + 4 H2O |
FFA : Free fatty acid
Table 1. Substrate specificity
| Substrate | Relative activity (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| CENII | CEN (T-18) | |
| Cholesterol Acetate C 2:0 | 22.6 | 21.1 |
| Cholesterol Propionate C 3:0 | 27.7 | 28.1 |
| Cholesterol Butyrate C 4:0 | 78.3 | 78.9 |
| Cholesterol Palmitate C 16:0 | 37.9 | 42.2 |
| Cholesterol Stearate C 18:0 | 13.2 | 13.0 |
| Cholesterol Oleate C 18:1 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| Cholesterol Linolate C 18:2 | 80.9 | 78.1 |
Table 2. Effect of detergents on CENII activity
| Additives | Concentration | Relative activity (%) |
|---|---|---|
| None | - | 100 |
| NiCl | 1mM | 67 |
| MnCl2 | 1mM | 101 |
| (NH4)2SO4 | 1mM | 107 |
| MgCl2 | 1mM | 106 |
| ZnCl | 1mM | 87 |
| ZnSO4 | 1mM | 81 |
| Ba(CH3COO)2 | 1mM | 106 |
| CaCl2 | 1mM | 114 |
| MoSO4 | 1mM | 69 |
| CuSO4 | 0.5mM | 3 |
| CuCl2 | 0.5mM | 0 |
| FeCl3 | 1mM | 102 |
| CoCl2 | 1mM | 86 |
| Li2CO3 | 1mM | 100 |
| CH3COOT | 1mM | 104 |
| EDTA | 1mM | 101 |
| KCl | 0.1M | 97 |
| NaCl | 0.1M | 98 |
| NaN3 | 0.05% | 102 |
| NaF | 20mM | 98 |
Table 3. Effect of detergents on CENII activity
| Detergent (0.3%) | Relative activity (%) |
|---|---|
| None | 100 |
| TritonX-100 | 147 |
| Adekatol TN-100 | 146 |
| Adekatol SO-120 | 142 |
| Newcol 707 | 146 |
| Newcol 710 | 139 |
| Emulgen 120 | 144 |
| Emulgen 705 | 159 |
| Sodium cholate | 103 |
| Deoxycholic acid | 128 |
| Sodium dodecyl sulfate | 1.1 |
| Sucrose fatty acid ester | 144 |
Table 4. Effect of detergents on CENⅡ activity when switching from Triton X-100 to other detergents
| Detergent (0.3%) | Relative activity (%) |
|---|---|
| TritonX-100 | 100 |
| Adekatol SO-120 | 61 |
| Adekatol SO-135 | 69 |
| Adekatol TN-100 | 82 |
| Adekatol PC-8 | 81 |
| Tween 20 | 1 |
| Tween 40 | 1 |
| Tween 80 | 1 |
| Sodium Cholate | 0 |
| Brij 35 | 2 |
| CHAPSO | 0 |
| Benzyltriethylammonium Chloride | 1 |
| Sodium dodecyl sulfate | 0 |
| Emulgen LS-110 | 30 |
| Newcol 710 | 13 |
| None | 0 |
Assay
Principle
-
The assay is based on the increase in absorbance at 493 nm as the formation of quinoneimine dye proceeds in the following reactions:
| CENII | ||
| Cholesterol ester+H2O | → | Cholesterol+Fatty acid |
| CO | ||
| Cholesterol+O2 | → | △4–Cholesten–3–one+H2O2 |
| POD | ||
| 2H2O2 +4 –AA +Phenol | → | Quinoneimine dye + 4 H2O |
Unit definition
-
One unit is defined as the amount of enzyme which liberates 1 μmole of cholesterol per minute at 37°C under the conditions specified in the assay procedure.
Reagents
- Reaction mixture
0.2M KH2PO4–NaOH buffer pH 6.8 0.60 ml 0.35%(W/V)4–AA solution 0.30 ml 0.2%(W/V)Phenol solution 0.30 ml 100 U/ml POD solution1) 0.30 ml 3%(W/V)Triton X–100 solution 0.30 ml 0.2 U/ml CONⅡ solution2) 0.60 ml
Substrate solution3)
0.30 mlDistilled water 0.30 ml 1): 100 U/ml POD solution
Dissolve 1000 U(PPU)of POD with 10 ml of distilled water.2): 0.2 U/ml CONII solution
Dissolve 2 U of CONII with CONII dilution buffer ※)※): CONII dilution buffer
0.1 M KH2PO4–Na2HPO4 buffer pH 7.0 containing 0.05%(W/V)Triton X–100.3): Substrate solution
Calf serum - Enzyme dilution buffer
10 mM KH2PO4–NaOH buffer pH 7.5 containing 0.1%(W/V)bovine serum albumin(BSA). - Reagents
Triton X–100 : The Dow Chemical Company
CONII : Asahi Kasei Pharma Corporation #T– 84
Calf serum: GIBCO Co.(USA)
BSA: Millipore Fraction V pH 5.2 #81–053
4– AA: NACALAI TESQUE, INC. Special grade #01907–52
POD: Sigma Chemical Co. Type II #P–8250
Enzyme solution
-
Accurately weigh about 20 mg of the sample and add enzyme dilution buffer to make a total of 20 ml. Dilute it with enzyme dilution buffer to adjust the concentration to within 0.3–0.5 U/ml.
Procedure
- Pipette accurately 3.0 ml of reaction mixture into a small test tube and preincubate it at 37°C.
- After 10 min, add 50 μl of enzyme solution and mix to start the reaction at 37°C.
※ In the case of a test blank, add 50 μl of enzyme dilution buffer in place of enzyme solution. - After starting the reaction, measure the rate of increase per minute in absorbance at 493 nm. The rate must be measured within the linear portion of the absorbance curve.
-
△A/min =(As/min−Ab/min)≦ 0.050 Abs/minAbsorbance sample : As/min blank : Ab/min
Calculation
- Activity(U/mg of powder)= {(△A/min)/(12.0×1/2)} × 3.05/0.05 × 1/x
12.0 : millimolar extinction coefficient of quinoneimine dye at 493 nm(cm2/μmole) 1/2 : a multiplier derived from the fact that 2 mole of H2O2 produce 1 mole of quinoneimine dye 3.05 : final volume(ml) 0.05 : volume of enzyme solution(ml) X : concentration of the sample in enzyme solution(mg/ml)
Storage
-
Storage at –20°C in the presence of a desiccant is recommended. Enzyme activity will be retained for at least one year under this condition(Figure 5)
References
- Bradford, M. B.,(1976)Anal. Biochem., 72, 248–254.
- Allain, C. C., Poon, L. S., Chan, C. S. G., Richmond, W.and Fu, P.C.(1974)Clin. Chem., 20, 470–475.
- Kameno, Y., Nakano, N. and Baba, S.(1976)Japanese
Journal of Clinical Pathology, 24, 650.
CENII 活性測定法(Japanese)
試薬液
- 反応試薬混合液
0.2M KH2PO4–NaOH 緩衝液 0.60 ml 0.35%(W/V)4–AA 溶液 0.30 ml 0.2%(W/V)フェノール溶液 0.30 ml 100U/ml POD 溶液1) 0.30 ml 3%(W/V)トリトン X–100 溶液 0.30 ml 0.2U/ml CONII溶液2) 0.60 ml
基質溶液3)
0.30 ml精製水 0.30 ml 1): 100U/ml POD 溶液
POD 1,000 単位(PPU)を精製水 10ml で溶解する。2): 0.2U/ml CONII溶液
CONII 2 単位(U)を CONII溶解用液※)10ml で 溶解する。※): CONII溶解用液
0.05%(W/V)トリトン X–100 を含む 0.1M
KH2PO4–Na2HPO4 緩衝液 pH7.03): 基質溶液
仔牛血清液 - 酵素溶解希釈用液
0.1%(W/V)BSA を含む 10mM KH2PO4–NaOH
緩衝液 pH7.5 - 試薬
トリトン X–100:Dow Chemical 製
CONII(コレステロール酸化酵素):旭化成ファーマ製 #T–84
仔牛血清液(Calf serum):GIBCO(USA)製
BSA: Millipore 製 Fraction V pH5.2 #81–053
4–AA:ナカライテスク製 特級 #01907-52
POD:シグマ製 Type II #P–8250
酵素試料液
- 検品約 20mg を精密に量り、酵素溶解希釈用液に溶解して全容 20ml とする。
その液を酵素溶解希釈用液で 0.3~0.5U/ml 濃度とな るように適宜希釈する。
測定操作法
- 小試験管に反応試薬混合液を 3.0ml 正確に分注して37°Cで予備加温する。
- 10 分経過後、酵素試料液 50 μl を正確に加えて混和し、37°Cで反応を開始する。
※ 盲検は酵素試料液の代わりに酵素溶解希釈用液50 μl を加える。 - 反応開始後、493nm における吸光度を測定して直線的に反応している 1 分間当たりの吸光度変化を求める。
求められた吸光度変化を試料液は As/min、盲検液は Ab/min とする。
ΔA/min =(As/min−Ab/min)≦ 0.050 Abs/min
計算
活性(U/mg)= {(△A/min)/(12.0×1/2)} × 3.05/0.05 × 1/x| 12.0 : | キノンイミン色素の 493nm におけるミリモル分子 吸光係数(cm2 /μmole) |
| 1/2 : | H2O22 モルからキノンイミン色素 1 モルが生成することによる係数 |
| 3.05 : | 反応総液量(ml) |
| 0.05 : | 反応に供した酵素試料液量(ml) |
| X : | 酵素試料液中の検品濃度(mg/ml) |