
Principle
Plastic optical fiber is a step-index multimode optical fiber, composed of a cylindrical "core" surrounded by a "clad" layer. The light refraction index of the core is higher than that of the clad. Light traveling through the core is therefore reflected at the core-clad interface, so long as the angle of its incidence with the interface is smaller than a certain "critical angle" (theta max). In this way, the light is repeatedly reflected from the interface as it progresses through the core to the end of the optical fiber.
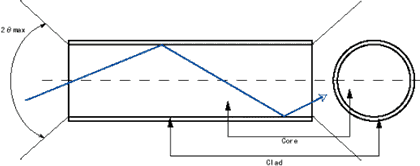
Transmission Characteristics
Plastic optical fibers transmit light efficiently throughout most of the visible spectrum (400 to 770 nm). Based on the characteristics of the PMMA core, plastic optical fibers show particularly low attenuation levels, of about 100 dB/km or less, for wavelengths of about 450 to 600 nm.
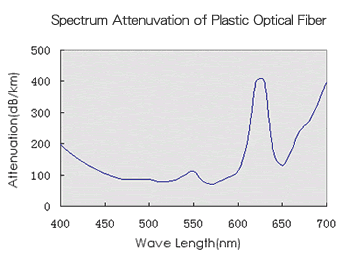
Sample fiber
Measurement: 52-2m cut-back method Incidental angle:0.15 rad.
- Specifications are subject to change without notice.