Break Through Trade-offs in Rubber Stopper Compounds with TUFTEC™
TUFTEC™ N527 is a promising primary material for compounding in medical rubber stopper applications. It balances the trade-offs of functionality, such as ease of needle insertion (low puncture resistance), prevention of liquid leakage after needle withdrawal (resealing property), and resistance to rubber being shaved off during puncture (core resistance), effectively achieving a balance between these features.
Achieve Easy Needle Insertion with N527’s Excellent Flexibility
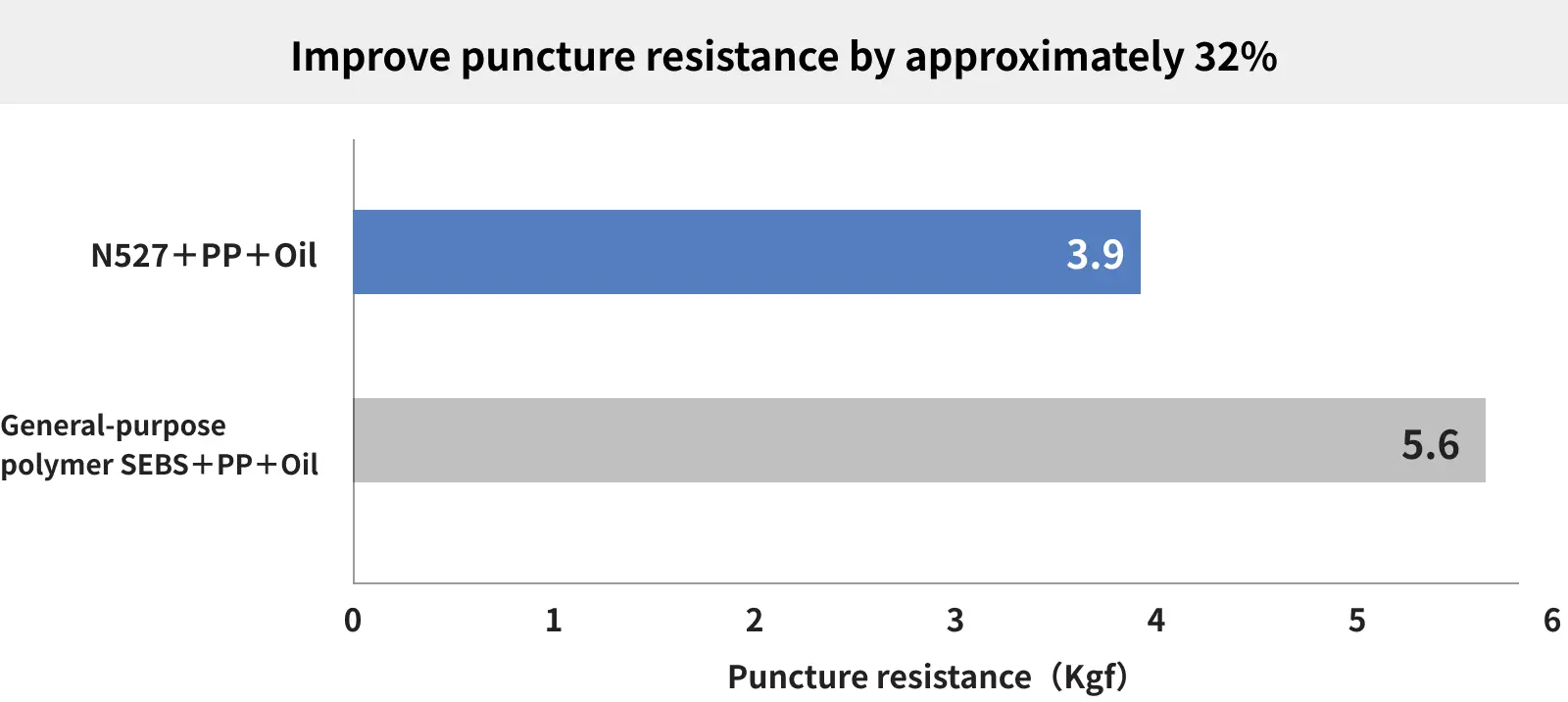
Rubber stoppers used for stoppers for, such as infusion drugs require easy needle insertion (low puncture resistance) for ease of use in the medical field. Rubber stoppers with high puncture resistance are hard and difficult to puncture with needles, requiring a considerable amount of force and affecting usability.
To achieve low puncture resistance in conventional rubber stoppers, a large amount of oil was used as a plasticizer to soften the material. However, if too much oil is added, there is a risk of it bleeding (dissolving) into the liquid over time.
TUFTEC™ N527 is more flexible than general-purpose SEBS polymers, allowing for the creation of rubber stopper compounds with low puncture resistance without the need for a large amount of oil. This prevents oil bleeding into the liquid.
Reduce Liquid Leakage After Needle Withdrawal with TUFTEC™ N527
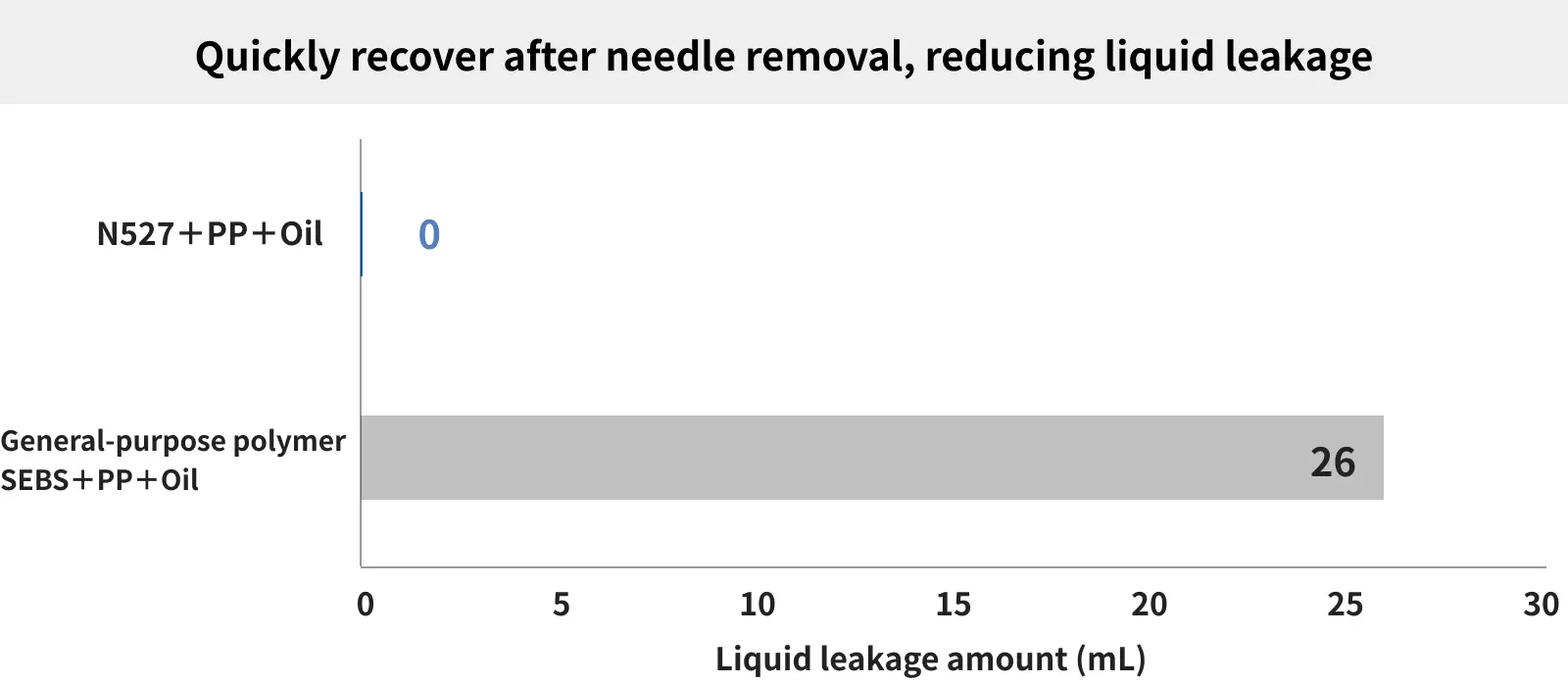
Rubber stoppers used in medical containers require “resealing properties” to reduce liquid leakage after needle withdrawal.
Rubber stoppers with poor resealing properties can leak liquid when the needle is withdrawn at the end of a procedure. This is why rubber stoppers require good recovery after needle withdrawal.
TUFTEC™ N527 has excellent recovery properties thanks to its low compression set (C-set), enabling high resealing properties in rubber stoppers to reduce liquid leakage after needle withdrawal.
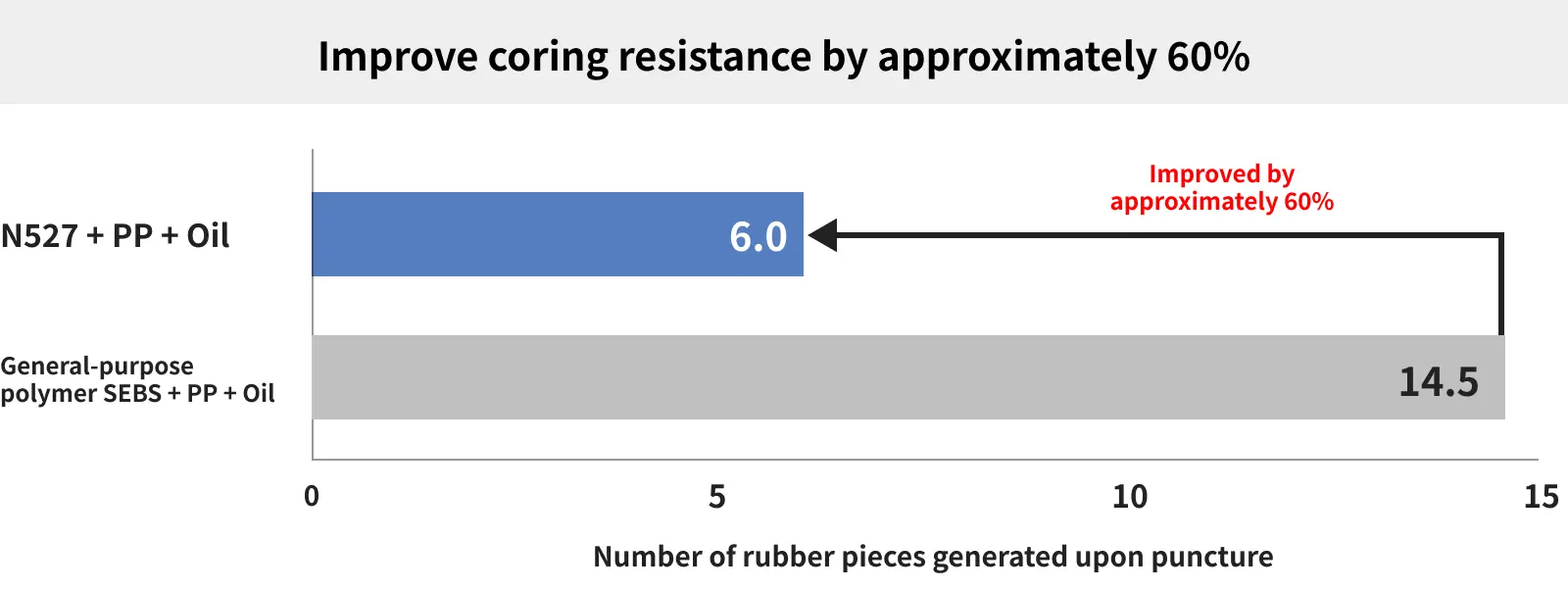
Improve Core Resistance During Puncture with Excellent PP Compatibility
Rubber stoppers require “core resistance,” the ability to resist rubber shavings during puncture. Rubber stoppers with poor core resistance can have rubber shavings attach to the needle during puncture, posing a risk of rubber fragments mixing into the liquid.
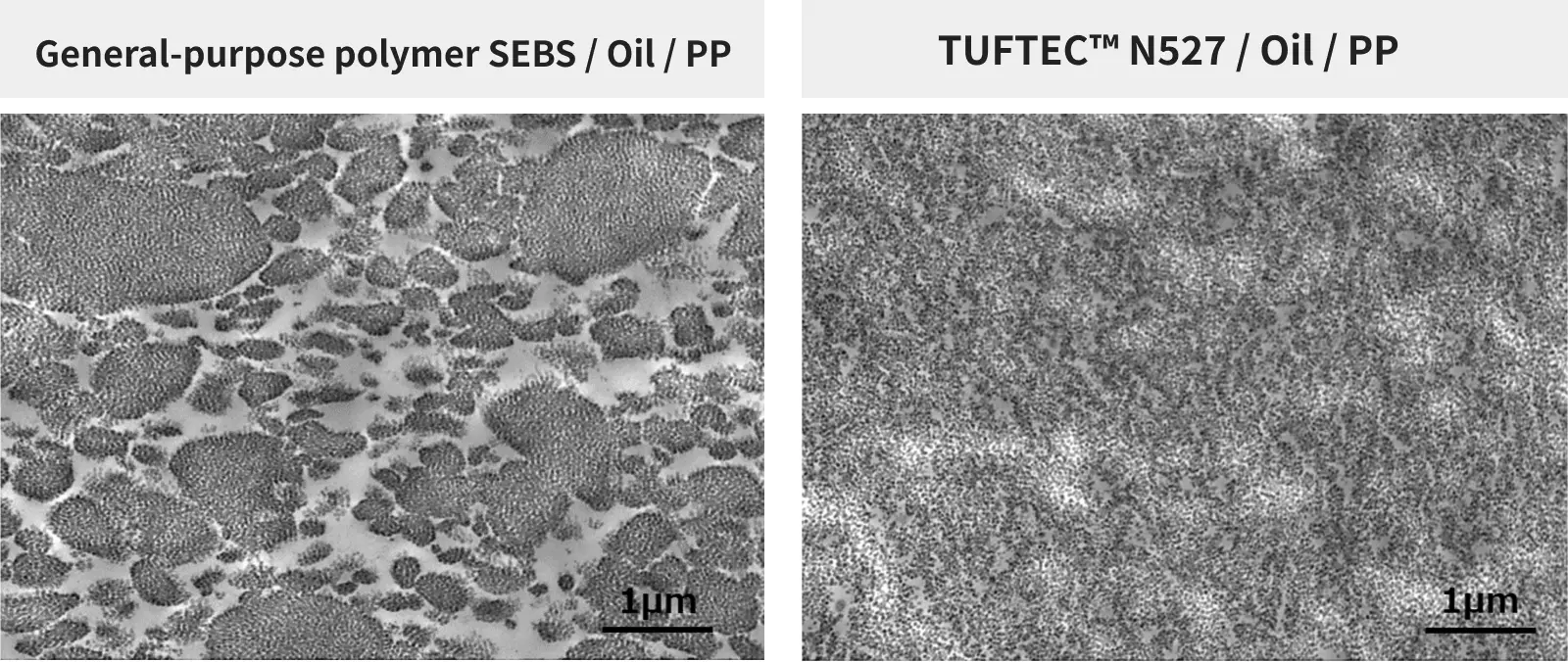
Core resistance can be improved by reducing the amount of oil in the rubber stopper compound to increase strength or increasing the amount of PP to increase sliding properties, but this increases the hardness of the compound, making it difficult to puncture with a needle. This leads to a trade-off where puncture resistance increases.
TUFTEC™ N527 has excellent compatibility with PP, contributing to the flexibility of the elastomer compound. Furthermore, since N527 itself is a material with sufficient flexibility, core resistance can be improved without sacrificing puncture resistance, even with a low oil content.