Safe and High-Performance Medical Tubes Enabled by TUFTEC™ and S.O.E.™
Asahi Kasei's S.O.E.™ and TUFTEC™/polypropylene blends are suitable for molding safe and high-performance medical tubes. These materials deliver a high level of functionality required for medical tubes while offering new added value, such as plasticizer-free and low drug adsorption properties, which are difficult to achieve with PVC.
Gaining Attention as PVC Alternatives for Medical Tubes
Medical tubes are primarily made from flexible polyvinyl chloride (PVC), but attention is turning to materials other than PVC due to concerns about drug adsorption, plasticizer migration, and environmental impact.
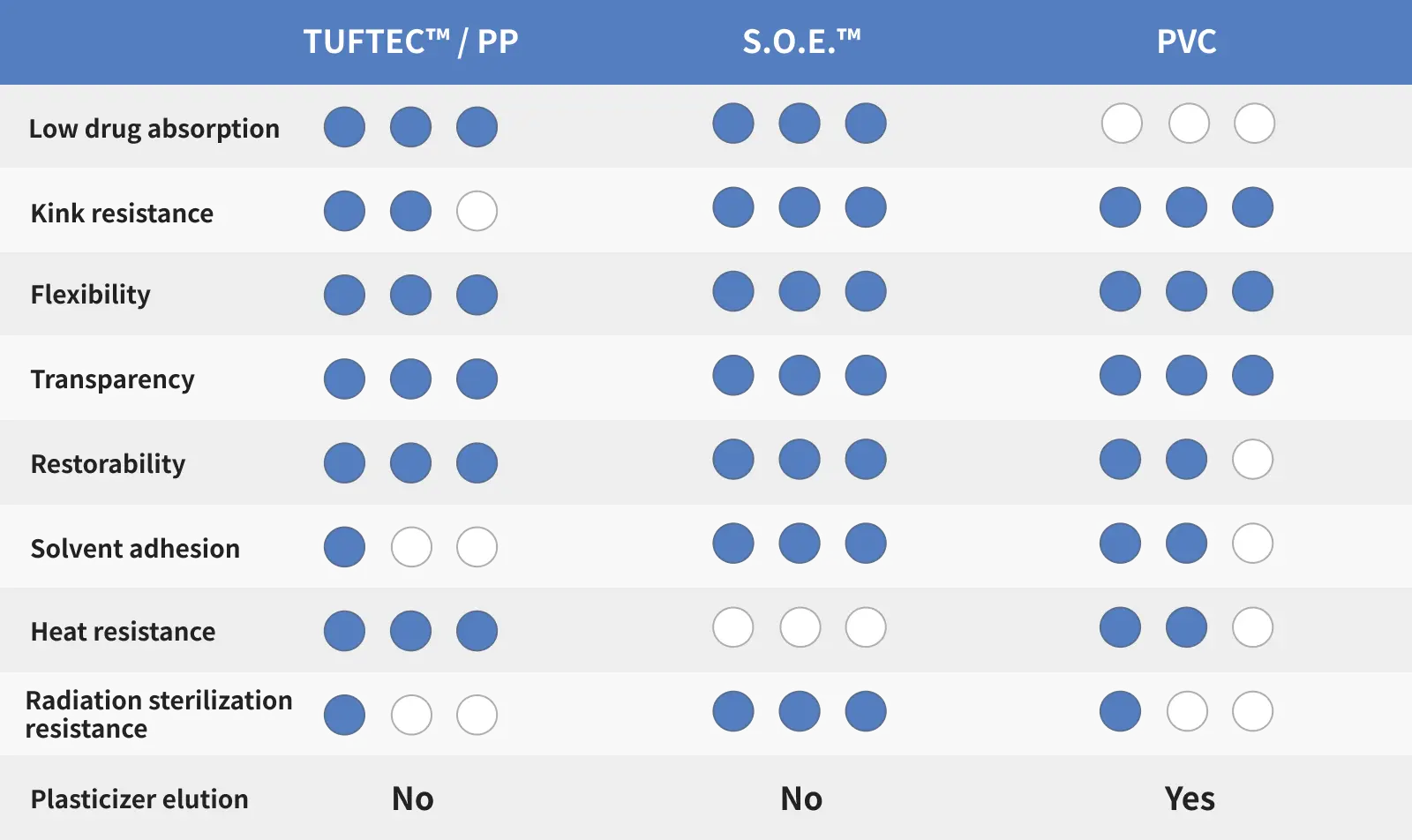
Asahi Kasei's S.O.E.™ and TUFTEC™ are "PVC alternative materials" that possess various functionalities required for medical tubes at a high level, as shown in the table below.
Furthermore, unlike PVC, S.O.E.™ and TUFTEC™ achieve high flexibility without plasticizers. This eliminates the risk of plasticizers leaching from the tube into the drug solution. Additionally, they exhibit low adsorption of drugs in the solution, offering the advantage of more quantitative drug administration.
The following sections will introduce the characteristics of medical tubes using S.O.E.™ and TUFTEC™.
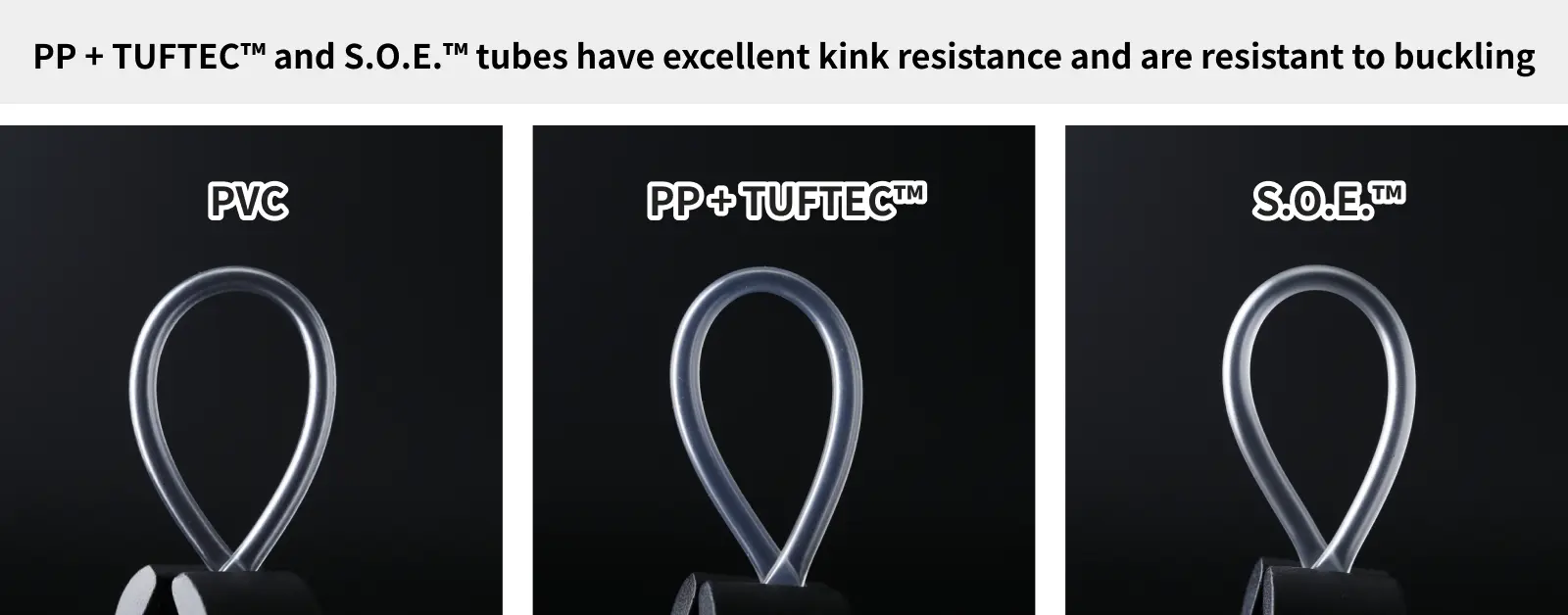
S.O.E.™ Tubes with Excellent Solvent Adhesion and Kink Resistance
S.O.E.™ is a SEBS that can be molded into tubes by itself. Compared to medical tubes made from conventional flexible polyvinyl chloride (PVC), it offers the following advantages:
-
High Solvent AdhesionS.O.E.™ tubes exhibit excellent solvent adhesion, demonstrating high bonding strength to polycarbonate and ABS. Therefore, they exhibit high adhesion for joining materials using solvents (such as drip bottles and connectors).
-
High Kink ResistanceS.O.E.™ tubes are designed to have a glass transition temperature (Tg) near room temperature by copolymerizing a soft segment, resulting in a large stress relaxation around room temperature and achieving excellent kink resistance. This characteristic makes the tube less prone to kinking, which is a common problem in medical settings, reducing instability during drug administration.
TUFTEC™/PP Blend Tubes with Excellent Recovery and Heat Resistance
TUFTEC™ is also a SEBS that can be molded into medical tubes by blending it with polypropylene (PP). TUFTEC™ has high compatibility with PP, and blending with it allows for the creation of highly flexible and transparent medical tubes. Compared to medical tubes made from conventional PVC, it offers the following advantages:
-
High Recovery After ClampingTUFTEC™ offers excellent flexibility and rubber elasticity, making it easy for the tube to return to its original shape after being clamped by forceps when the occlusion is released. This ensures stable fluid delivery.
-
Steam Sterilization PossibleTubes made from TUFTEC™/PP blends exhibit heat resistance. This enables the molding of medical tubes that can withstand autoclave sterilization at 121 degrees Celsius.
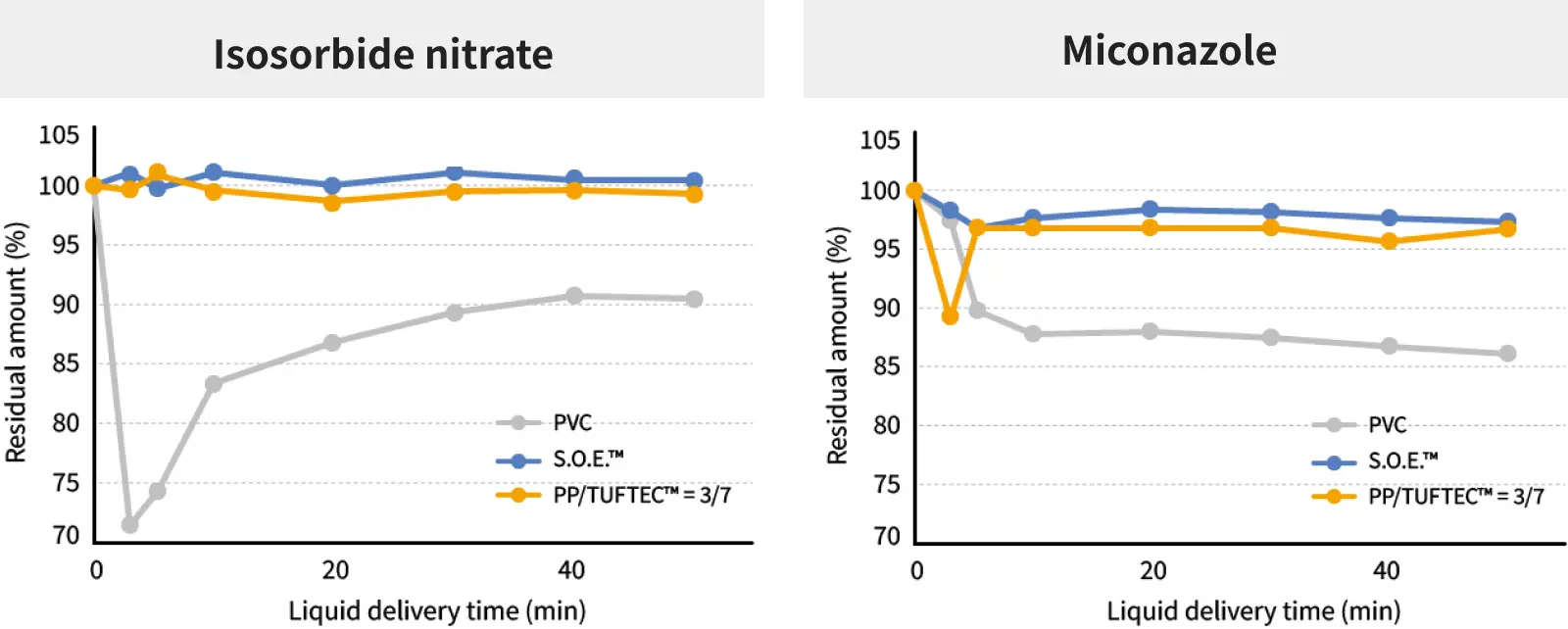
Low Drug Adsorption Enables Quantitative Drug Administration
Conventional medical tube materials, flexible polyvinyl chloride (PVC), have a high affinity with certain drugs, leading to drug adsorption onto the tube surface during passage, making it difficult to achieve reliable drug administration. TUFTEC™ and S.O.E.™ have lower polarity compared to PVC, minimizing drug adsorption to the tube and enabling quantitative drug administration.