- Overview
- Therapies
- Applied
Products - References
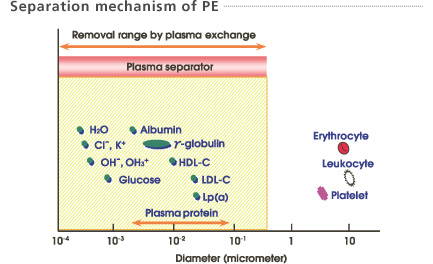
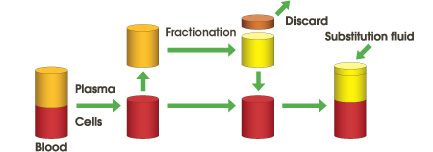
Blood is separated into plasma and blood cells using a membrane plasma separator (Plasmaflo OP). Separated plasma containing pathogenic substances is discarded and replaced with substitution fluid, e.g., albumin solution, or often fresh frozen plasma.
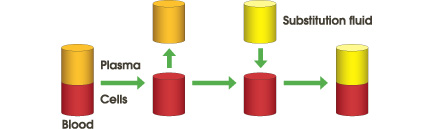
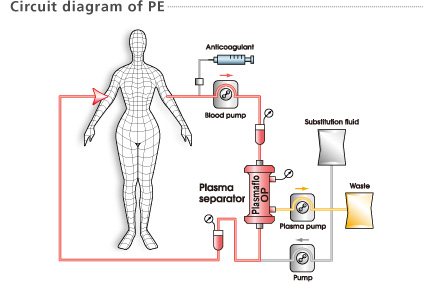
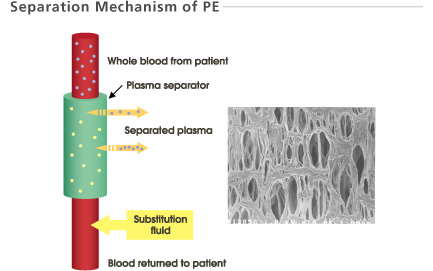
The large pores of the membrane allow plasma, proteins and pathogens to pass through and be discarded. Cells and platelets are retained. Substitution fluid is added and the treated blood is returned to the patient.
- Wide area of application
- Possible to exchange Cell-free plasma
- Low Platelet loss compared to Centrifugation
- Large amount of substitution fluid is required
- Possible protein allergy to substitution fluid
- Possible risk of infection from substitution fluid
- Reactions to membrane
Plasma, separated by a plasma separator (Plasmaflo OP) is then fractionated into large and small molecular weight components by a membrane type plasma component separator (Cascadeflo EC). Large molecular weight components including pathogenic substances are discarded. Small molecular weight components including valuable substances such as albumin are returned to the patient. It may be necessary to add a small amount of substitution fluid such as albumin.
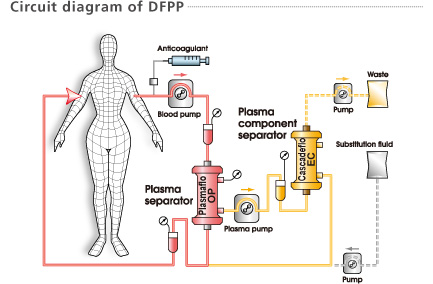
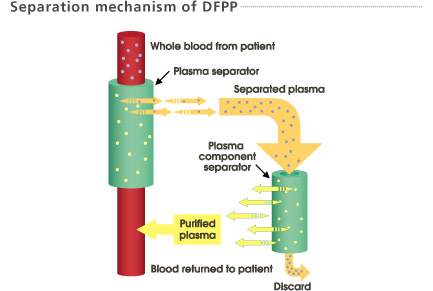
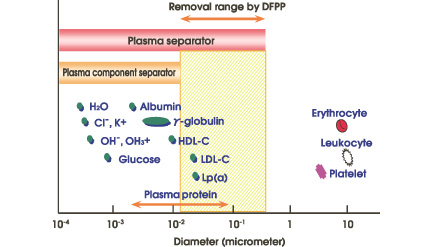
1. The large pores of the first filter membrane allow plasma, proteins and pathogens to pass through and into the second filter.
2. The second filter, of smaller pore size, selectively removes pathogenic substances from the plasma.
3. Substitution fluid may be added and the treated blood / plasma is returned to the patient.
4. Pathogenic substances and some plasma are discarded.
- More selective than Plasma Exchange
- Returns purified plasma to the patient
- Minimal loss of patient’s own desirable non-pathogenic substances
- Minimal Albumin loss
- Minimal substitution fluid required - no FFP
- Minimal risk of infection from substitution fluids
- Reduces possible protein allergy to substitution fluid
- Semi-selective
- Some “valuable” components of similar size and Molecular Weight to pathogen may also be lost
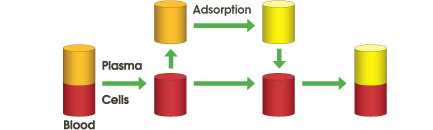
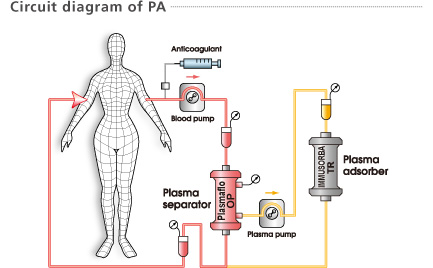
Plasma, separated by a plasma separator (Plasmaflo OP) passes through a plasma adsorption column (IMMUSORBA / PLASORBA). Pathogenic substances are adsorbed by affinity between the ligands and pathogenic substances. No substitution fluid is required.
Immunoadsorption (IA) is a subcategory of Plasma Adsorption (PA) because it follows the same method. It is referred to as IA when the adsorption column selectively adsorbs immune complexes and auto-antibodies.
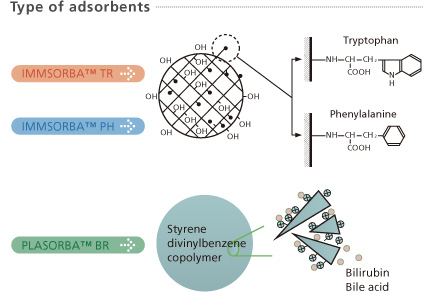
IMMUSORBA TR, PH
Removal of pathogens from separated plasma by adsorption onto amino acid ligand bound to PVA gel carrier bead. Adsorption is by Hydrophobic bonding.
PLASORBA BR
Removal of pathogens from separated plasma by ionic adsorption onto Styrene Divinyl Benzene Co-polymer beads.
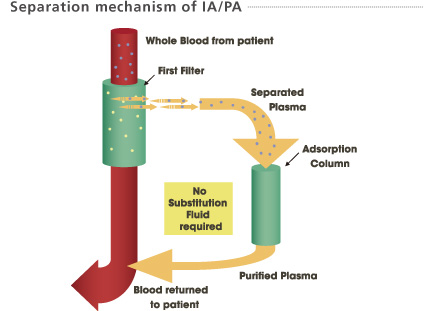
1. The large pores of the first filter membrane allow plasma, proteins and pathogens to pass through and into the adsorption column.
2. The adsorption column selectively removes pathogenic substances from the plasma.
3. The treated blood / plasma is returned to the patient.
- More selective than Plasma Exchange
- Selective removal based on Hydrophobic adsorption
- Ligand is physiological Amino Acid
- Returns purified plasma to the patient
- Minimal loss of patient’s own desirable non-pathogenic substances
- No substitution fluid required
- No risk of infection from substitution fluids
- Eliminates possible protein allergy to substitution fluid
- Suitable for patients with protein allergy
- Limited area of application
Needles are placed in peripheral veins. Single or double lumen catheters are also used in the internal jugular, subclavian or femoral veins.
The amount of plasma to be treated is usually the patient’s estimated plasma volume (EPV). EPV is calculated using the following formula.
EPV = BW x 1/13 x (1 - Ht/100)
BW: Body weight (kg)
Ht: Hematocrit (%)
Example) Patient BW = 65 kg, Ht = 40% ⇒ EPV = 3.0 Liter
Heparin or citrate (sodium citrate or ACD-A) is mainly used as an anticoagulant. The choice and dosage is decided by the responsible physician who is familiar with the anticoagulation regimen and knows the clinical condition of the patient.
The choice of substitution fluid is usually based upon the condition of the patient, cost, convenience and the volume required to replace the plasma removed during the exchange treatment. Albumin solution, or Fresh Frozen Plasma (FFP) are mainly used.
Please feel free to send us any questions you may have about our products and support.
Share your feelings and experiences when using our products.