Principle of Membrane Separation
There are several principles of membrane separation, such as pressure difference, concentration difference, and ion exchange. Here, separation by pressure difference is introduced.
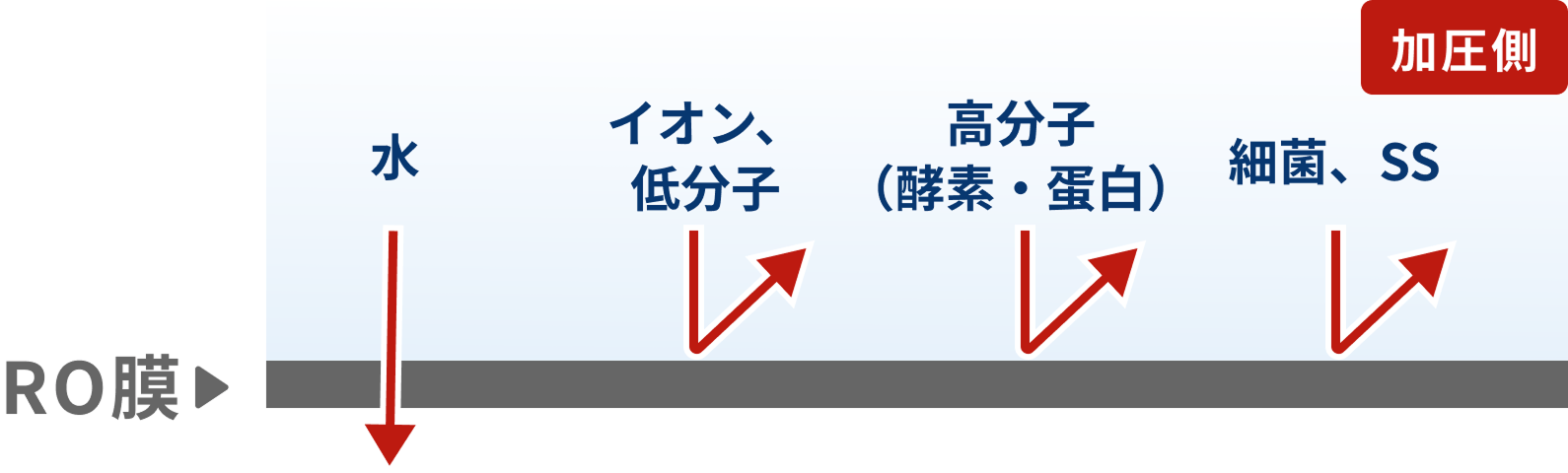
Separation by Pressure Difference RO (Reverse Osmosis)
An RO (reverse osmosis) membrane separates a concentrated solution and a dilute solution with a membrane. By applying a pressure greater than the osmotic pressure to the concentrated side, only water molecules pass through the membrane from the concentrated to the dilute side, enabling the separation of ions and low-molecular-weight organic substances.
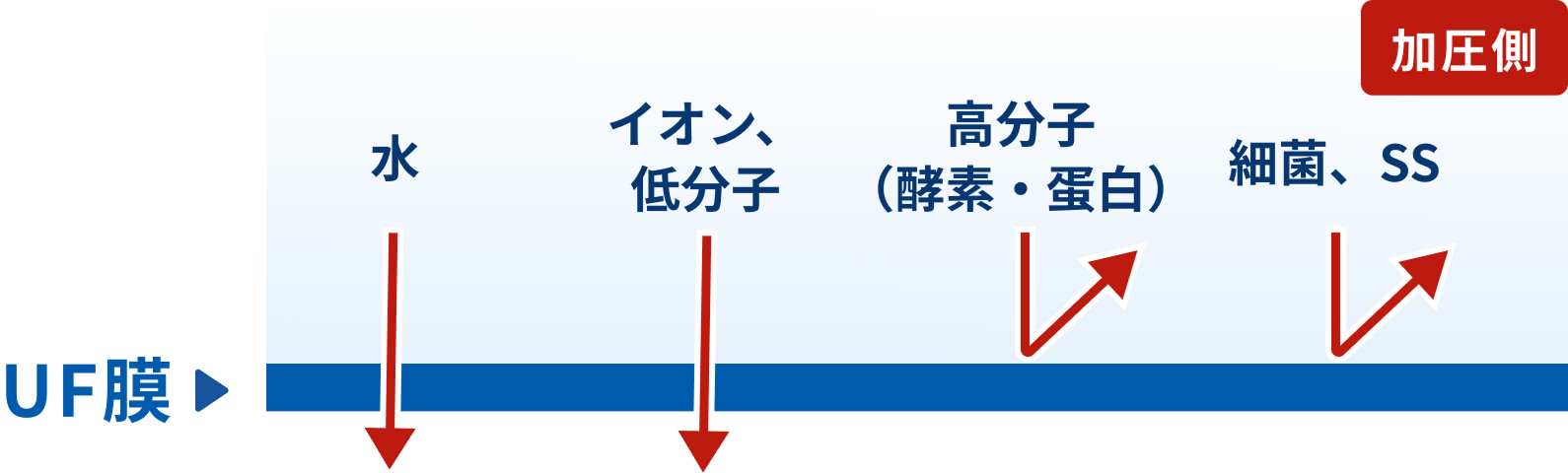
UF (Ultrafiltration)
A UF (ultrafiltration) membrane separates, fractionates, concentrates, and purifies solutes at the molecular level by sieving based on the membrane pore size and solute molecular size.
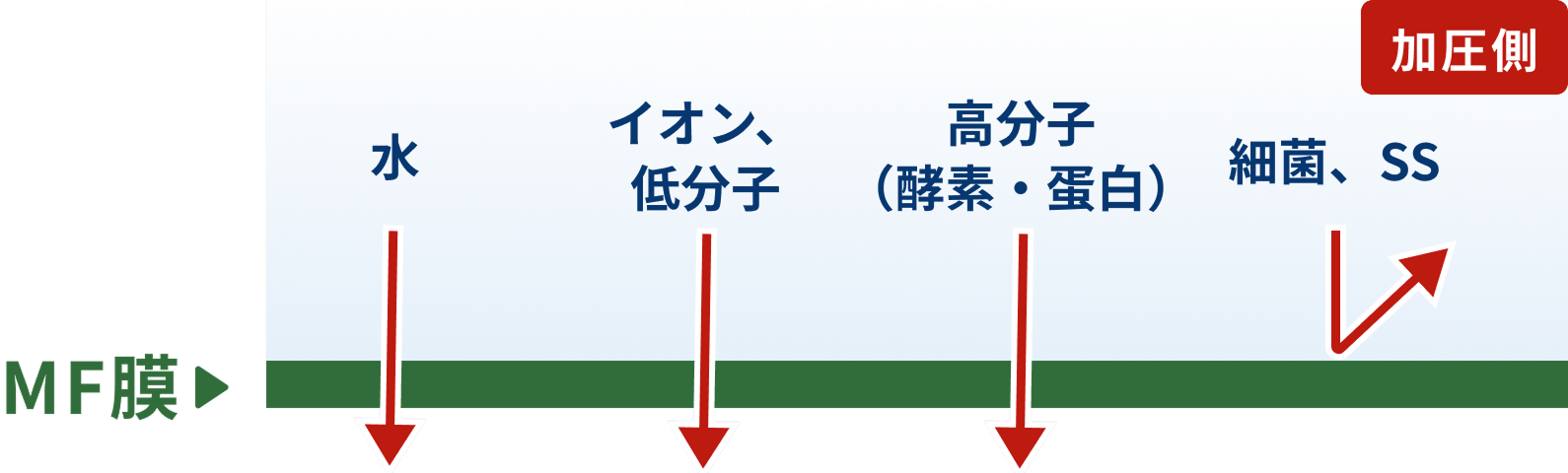
MF (Microfiltration)
MF (microfiltration) membranes are used to accurately and efficiently separate and purify suspended solids and colloidal particles in liquids.
Click here for tips on solving issues related to filtration and separation.
Asahi Kasei's hollow fiber membrane Microza® for filtration and separation is used in a wide range of fields, including pharmaceuticals, pharmaceutical water, food, chemicals, semiconductors, as well as power, water supply, and industrial water. Please see here for Microza® applications, solutions by industry, and case studies.