Asahi Kasei's Technical Expertise Supports Industrial Operations
Microza® is more than just a "membrane." It features robustness for stable long-term operation under demanding conditions, a variety of membrane materials and pore sizes, and high maintainability enabled by backwashing, among other technical and scientific advantages.
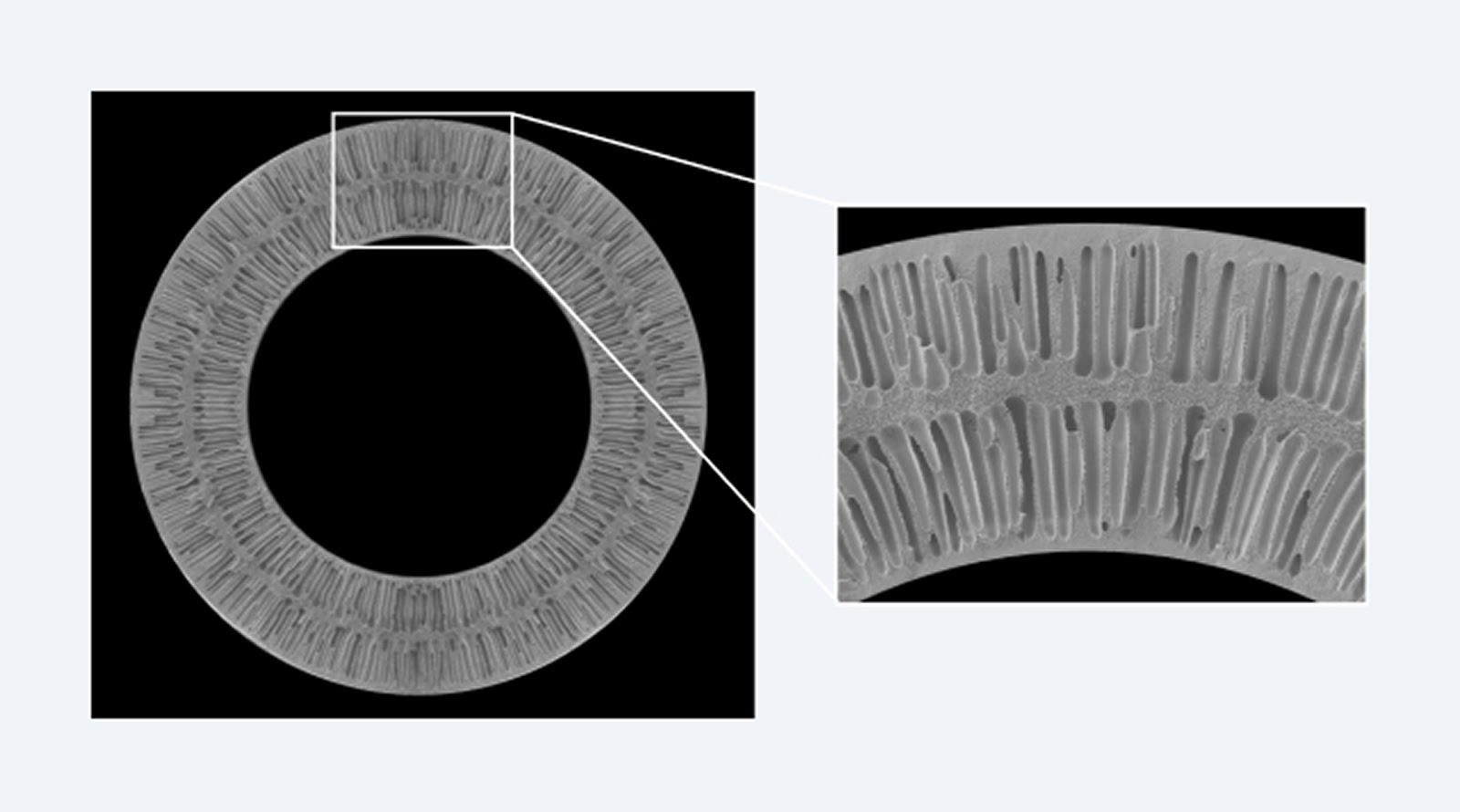
Advanced Membrane Fabrication Technology and Pore Size Control
One of Microza®'s core technologies is its membrane fabrication method. While PVDF membranes are commonly produced using the NIPS method (non-solvent induced phase separation), Microza® utilizes the TIPS method (thermally induced phase separation). This achieves high chemical resistance, durability, and strength over extended periods.
-
Benefits of the TIPS MethodBy adopting the TIPS method, the risk of leakage is greatly reduced even in harsh chemical environments such as oxidizers, alkalis, and strong acids. Improved crystallinity within the material enhances resistance to friction and mechanical stress. As a result, water permeability deteriorates more slowly during long-term operation, providing significant economic benefits by reducing maintenance frequency.
-
Precise Control of Pore Size DistributionA proprietary membrane formation process minimizes pore size variation between production lots. This maintains sharp separation accuracy and stable filtration performance. Uniform filtration quality is also ensured in large-scale plants, making it easier to maintain product consistency.
Double-Skin Structure Achieves Both High Filtration Performance and Durability (UF Membranes)
The risk of hollow fiber membrane damage directly affects stable plant operation, making reliability in durability extremely important. Microza®'s double-skin structure places skin layers (separation function layers) on both the inner and outer surfaces, providing significantly greater damage resistance compared to single-skin membranes.
-
Mechanism of the Double-Skin StructureThe double-skin structure forms ultra-thin layers on both the inner and outer surfaces of the hollow fiber membrane, achieving both high separation capability and abrasion resistance. If the inner surface is damaged, the outer membrane still functions, preventing immediate leakage.
| Comparison Item | Single-Skin Membrane | Double-Skin Membrane |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Separation layer only on the inner surface | Separation layers on both inner and outer surfaces |
| Damage Resistance | Low | High |
| Leak Risk | High | Low |
| Backwashability | Risk of damage under reverse pressure | Backwashable |
Enhanced Maintainability Through Backwashing, Chemical Cleaning, and Data Utilization
Excellent maintainability is essential for reducing membrane system running costs. Microza® enables safe and efficient backwashing and chemical cleaning through its double-skin structure and high-strength hollow fibers. Additionally, maintenance is further improved by optimizing replacement timing based on proprietary data and membrane analysis.
-
Backwashable Membrane DesignReverse pressure cleaning during system shutdown removes contaminants accumulated on the membrane surface. Setting a backwash cycle minimizes the decrease in water permeability during operation.
-
Proven Chemical Cleaning Performance and Broad pH ResistanceApplicable to a wide range of cleaning agents, including acids, alkalis, and chlorine-based cleaners. High recovery rates of water permeability after cleaning enable longer membrane life. Products are also available that withstand chlorine cleaning for RO membrane pretreatment.
-
Analytical Support for Stable OperationAsahi Kasei analyzes the performance of used membranes to accurately determine replacement timing. This contributes to overall reductions in manufacturing and disposal costs.